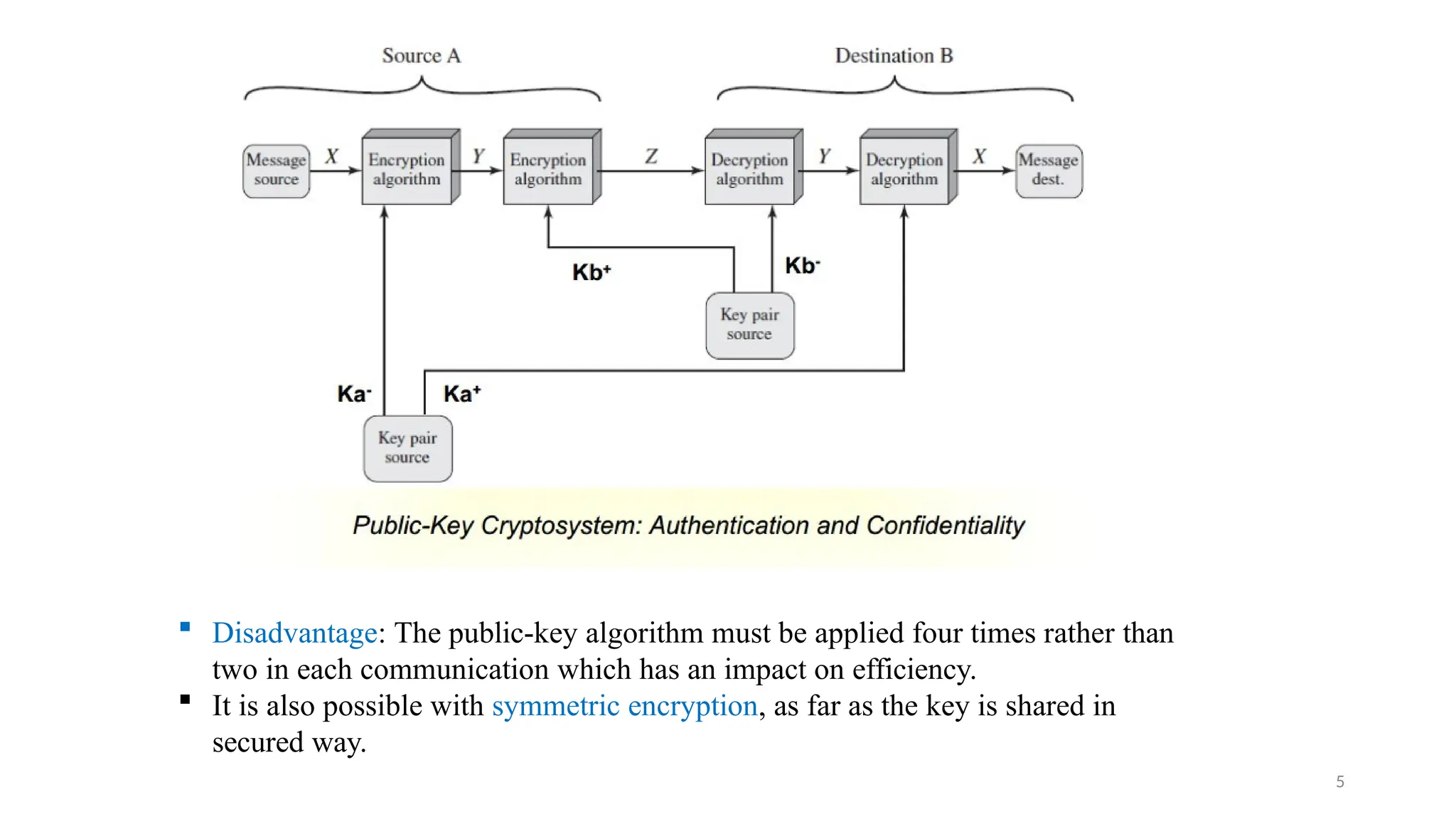
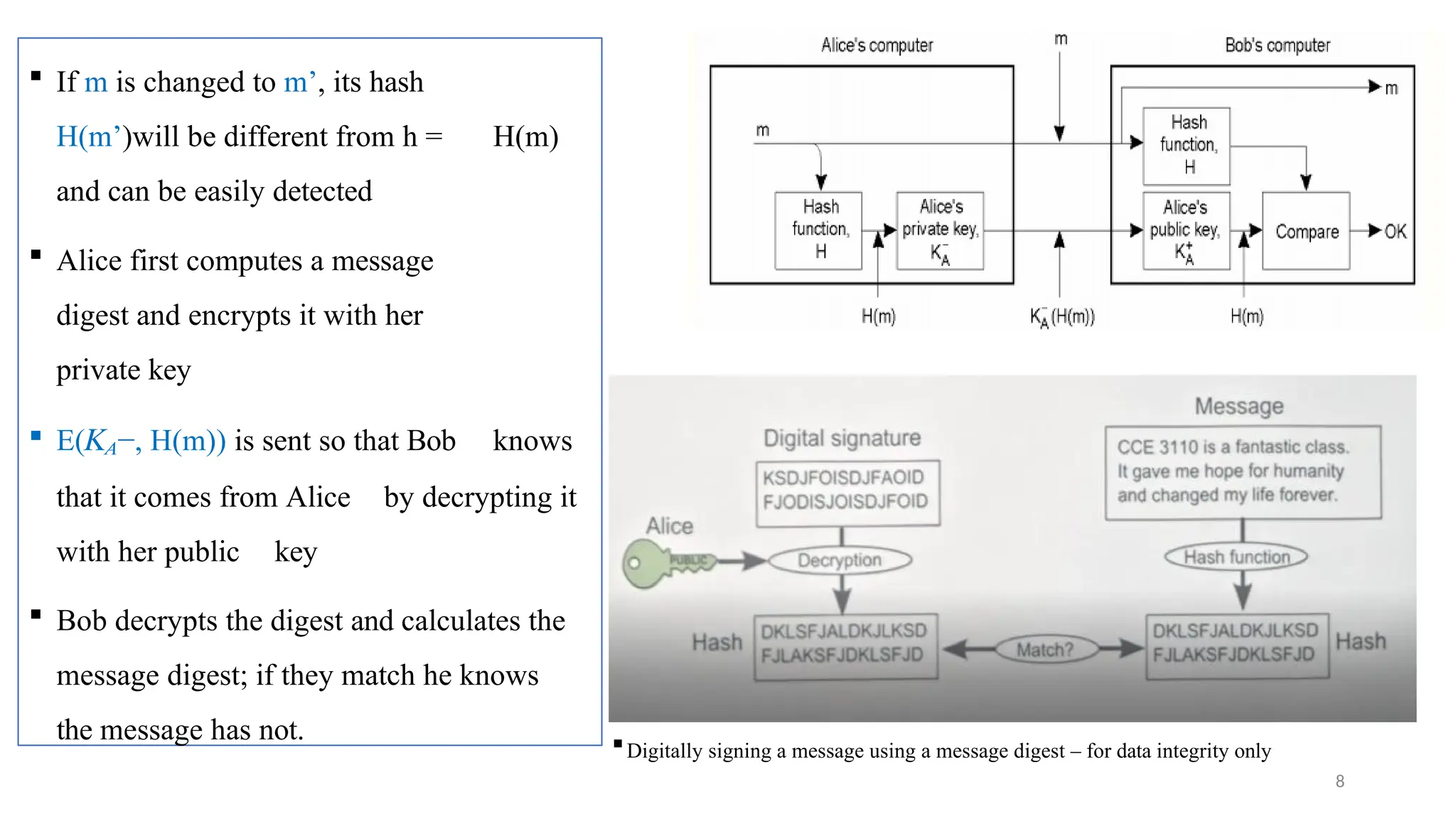
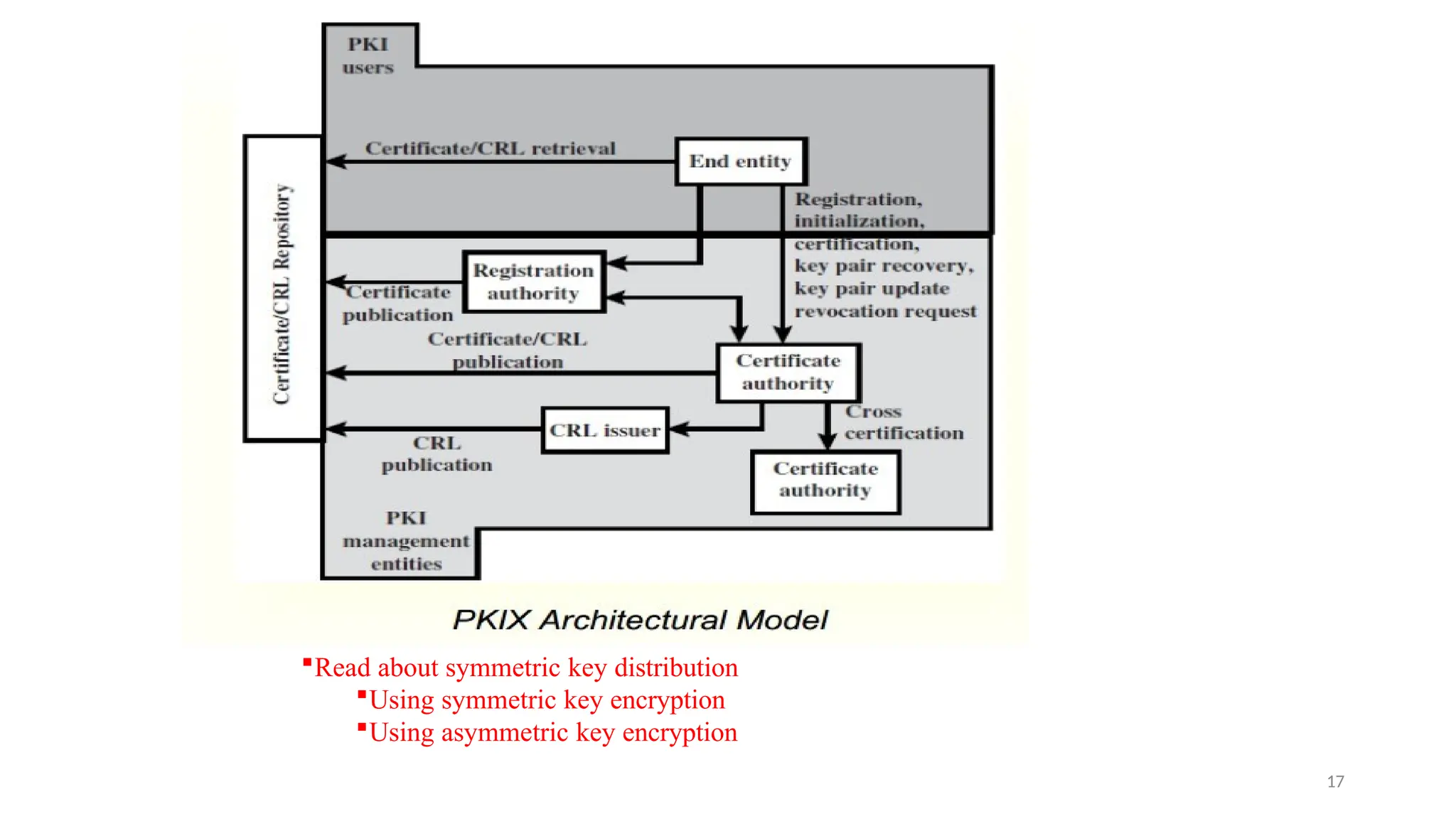
Digital signatures provide authentication and data integrity, proving the sender's identity and ensuring message authenticity without guaranteeing confidentiality. They reverse the encryption process using private and public keys, allowing verification and protection against unauthorized alterations. Popular hashing algorithms like MD5 and SHA produce message digests that facilitate efficient data integrity checks, while public-key infrastructure establishes trust through certification authorities.