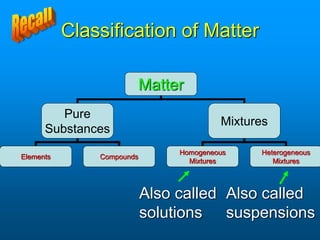
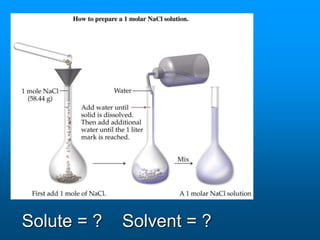
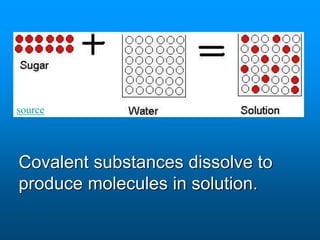
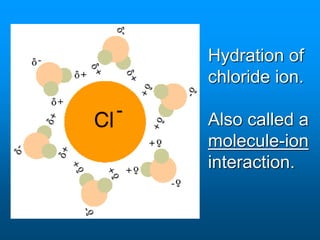
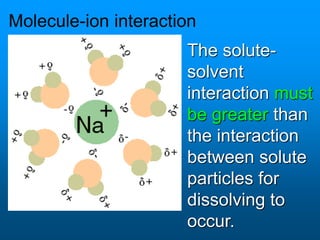
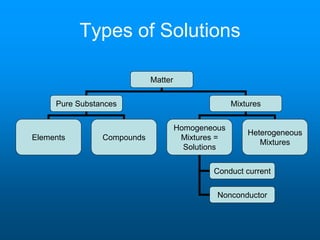
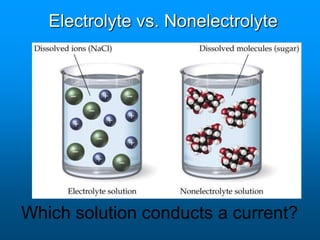
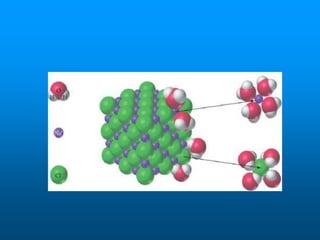
- A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, where the solute dissolves evenly throughout the solvent. The solute is the dissolved substance while the solvent is the dispersing medium.
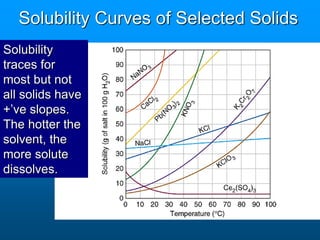
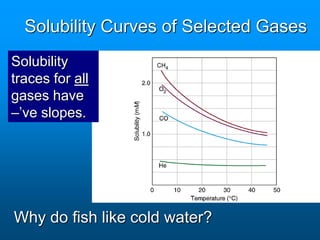
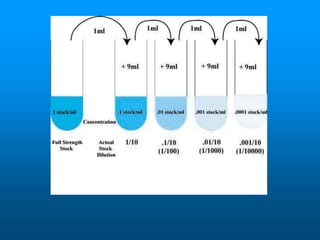
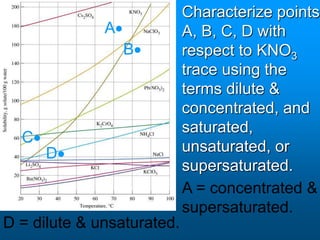
- The solubility of a substance refers to the maximum amount that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a certain temperature and pressure. Solubility curves graphically represent solubility.
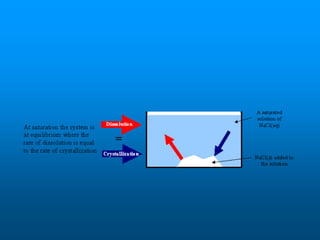
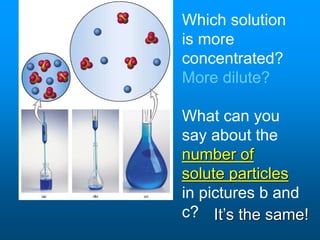
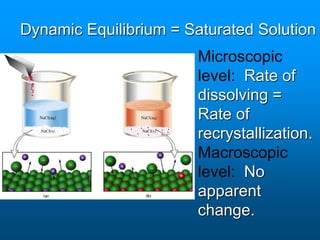
- Factors like temperature, pressure, and amount of solute already dissolved can impact the rate at which a substance dissolves or its solubility. A saturated solution contains as much solute as can dissolve whereas an unsaturated solution can dissolve more and a supersaturated solution contains more than expected.