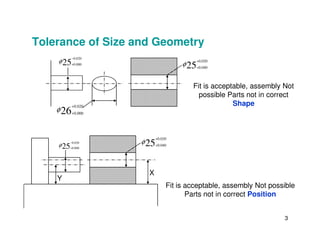
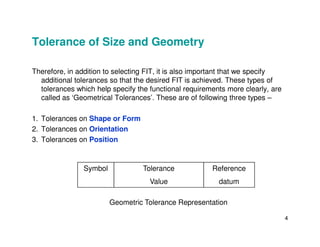
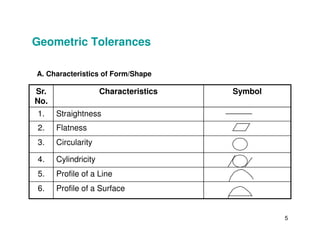
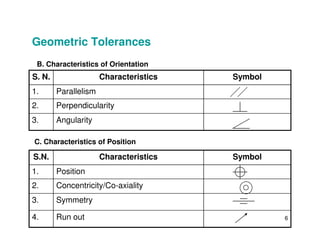
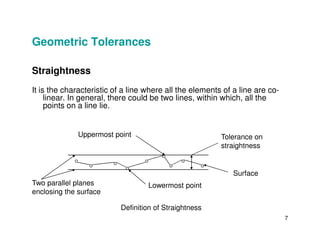
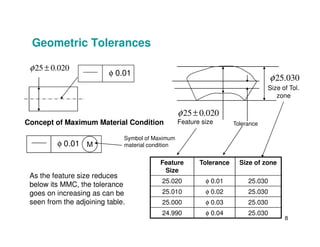
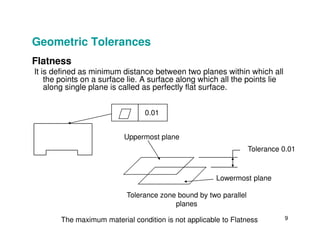
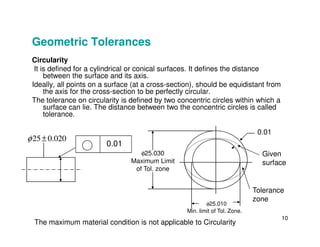
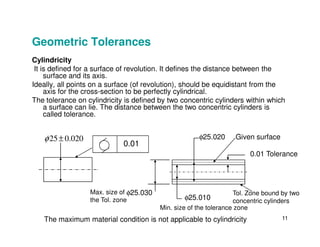
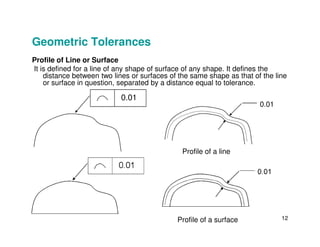
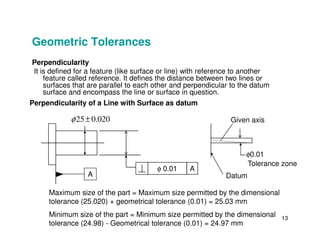
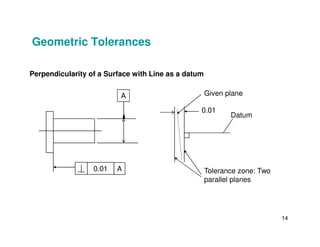
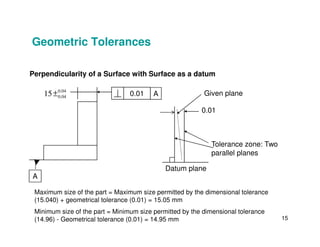
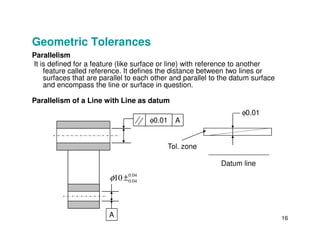
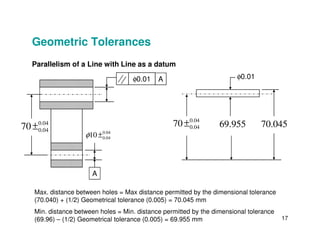
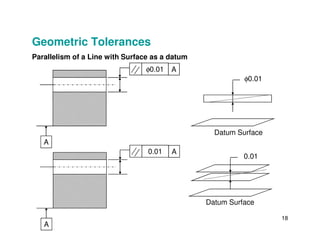
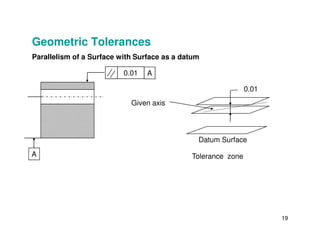
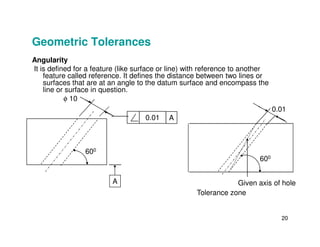
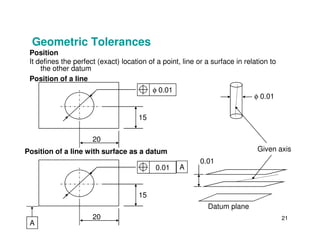
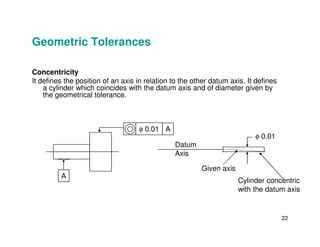
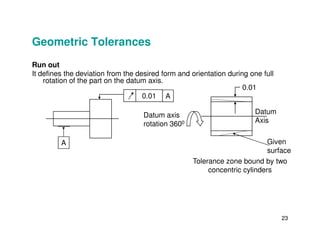
The document provides an overview of geometric tolerances, which specify functional requirements for manufactured parts beyond just size tolerances. It defines various geometric tolerances including: (1) tolerances on shape or form like straightness, flatness, circularity, and cylindricity; (2) tolerances on orientation like parallelism, perpendicularity, and angularity; and (3) tolerances on position like concentricity and symmetry. Examples are given to illustrate how each tolerance type places limits on a feature's allowable form, orientation, or location relative to a datum.