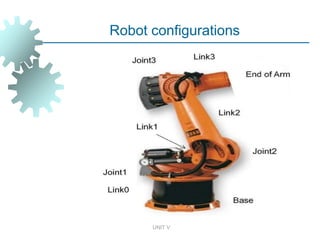
This document outlines the syllabus for the unit on robotics from a CAD CAM course. It discusses the history of prominent robot configurations like PUMA and SCARA robots. It also presents the three laws of robotics established by Isaac Asimov. The unit covers various robot drive systems, sensors used in robotics, programming techniques and languages. It lists applications of robots in material handling, assembly, inspection and more. Finally, it discusses latest developments in robot intelligence, sensors, mobility and uses of robots in hazardous environments, space, security, hospitals and households.