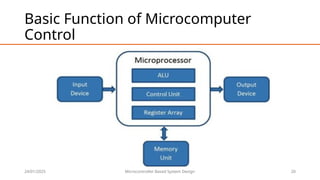
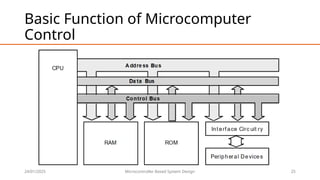
This document provides an overview of microcomputers, detailing their significance, history, and basic functions. It highlights the transition from large systems to accessible personal computing, the evolution of technology from the 1970s to modern-day microcomputers, and their applications in various fields. Key components and their functions, including data processing, communication, and automation, are also discussed.