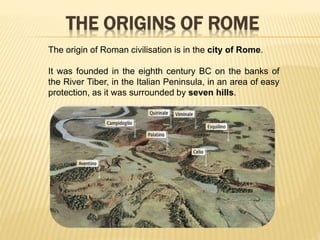
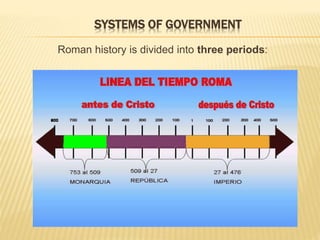
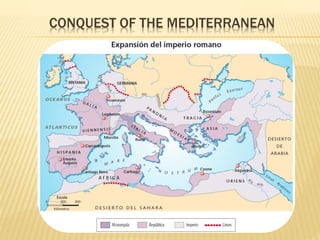
The document summarizes the origins and history of ancient Rome. It describes how Rome was founded in 753 BC by Romulus on the banks of the Tiber River. Rome was originally ruled by kings, then became a republic with elected magistrates and shared power between the comitias, magistrates, and senate. Eventually the republic transitioned into an empire beginning with Augustus in 27 BC. The empire reached its peak but then declined due to various political, economic, and social instabilities before finally falling in 476 AD.