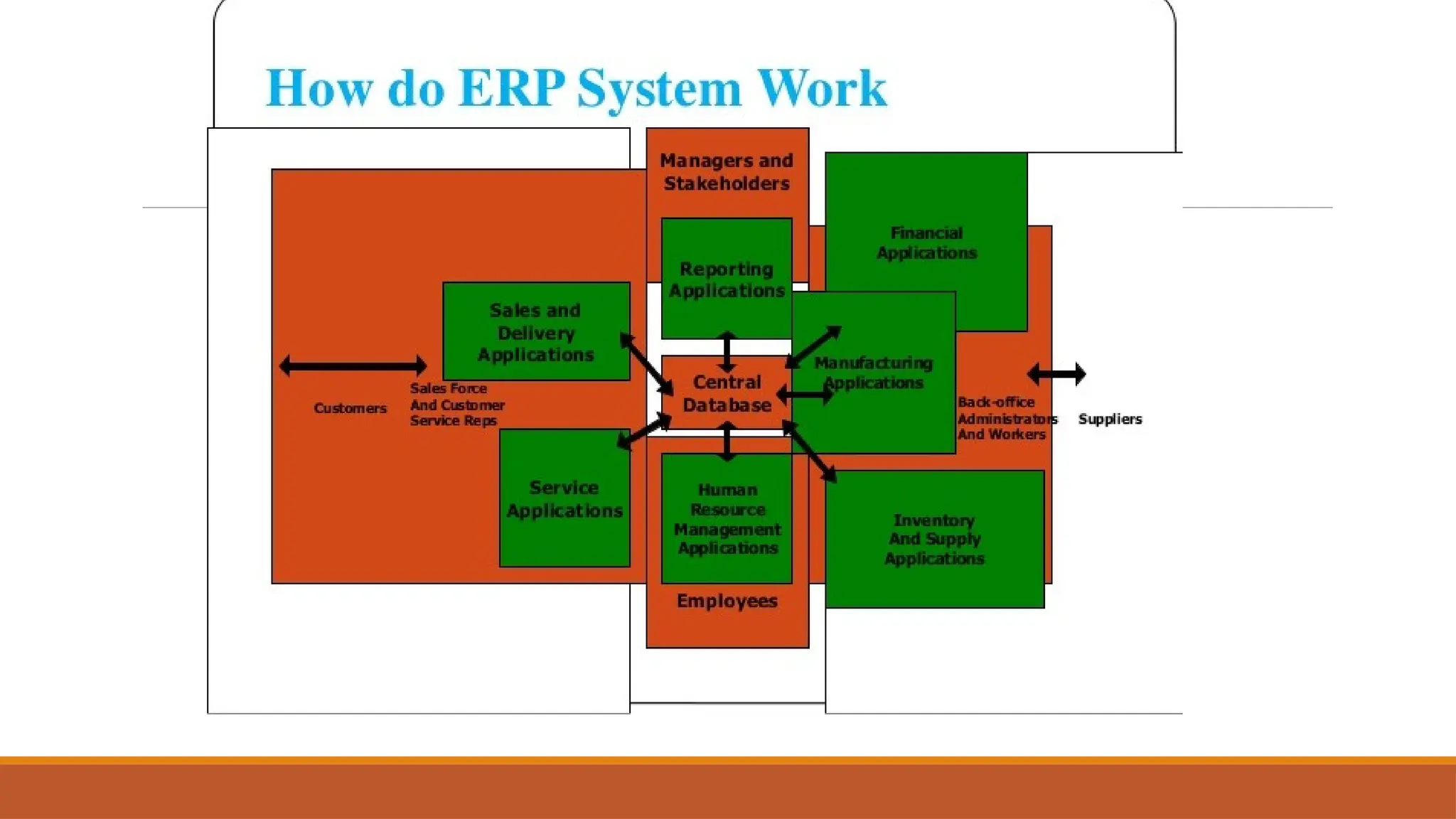
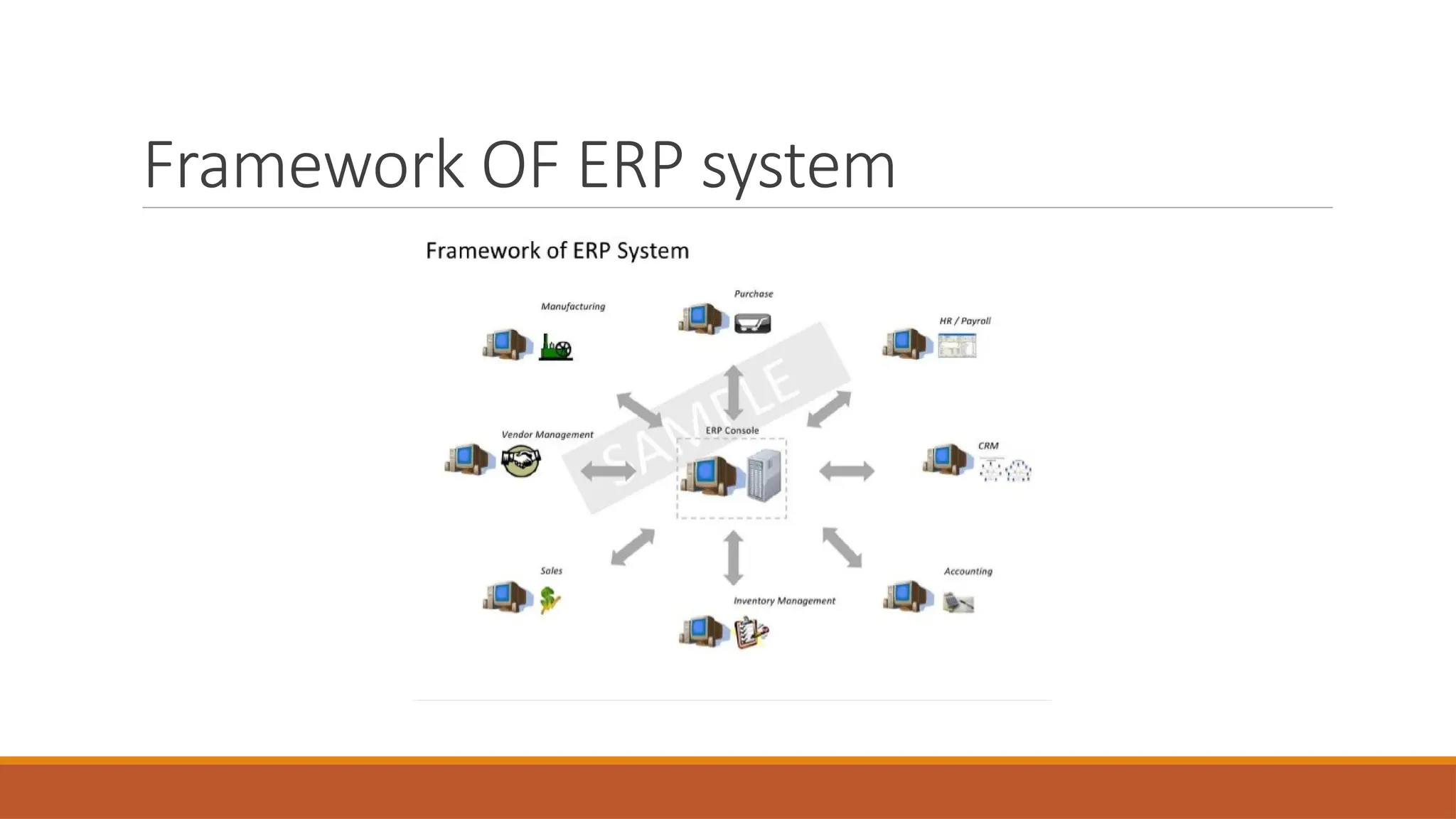
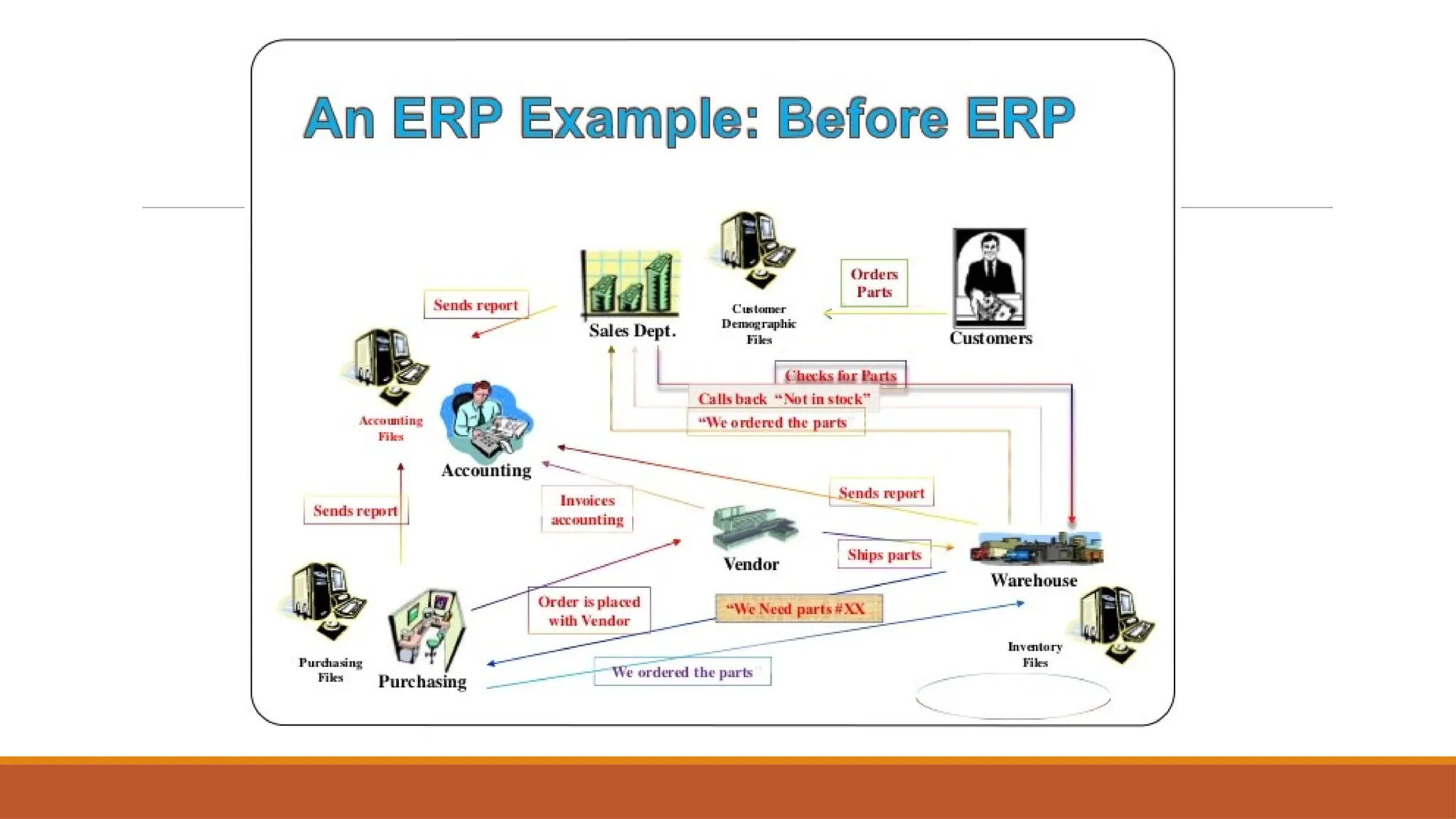
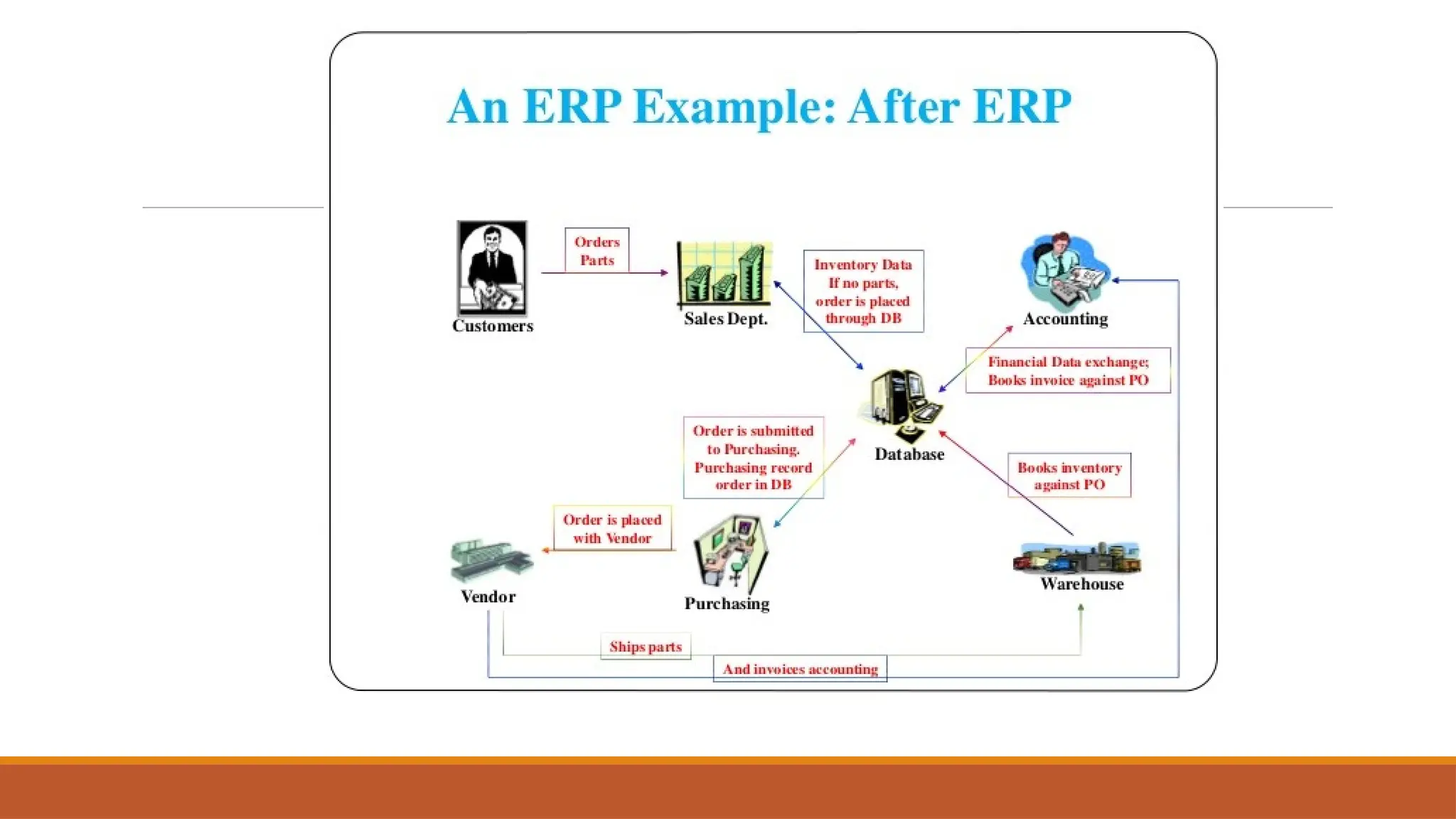
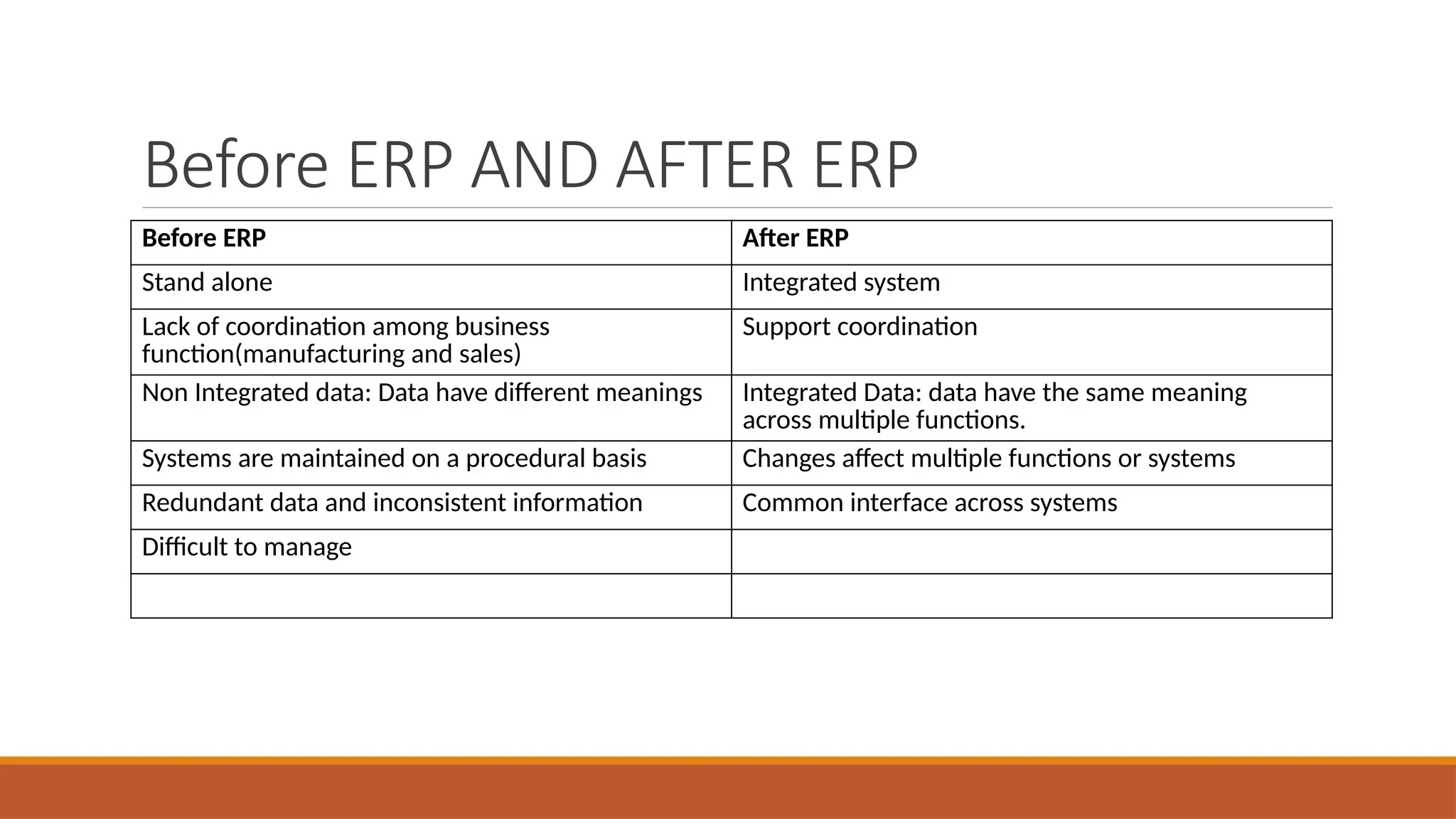
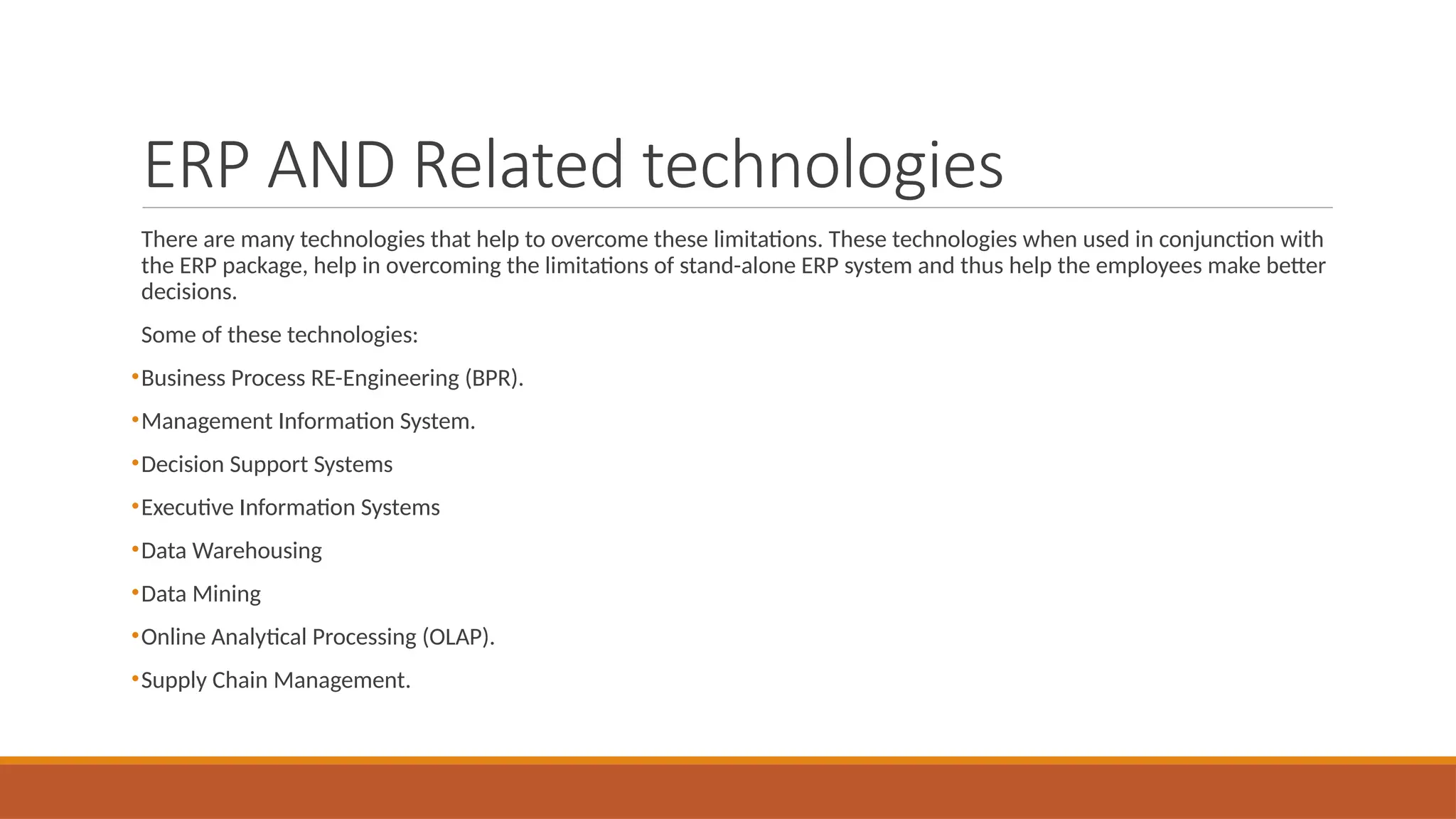
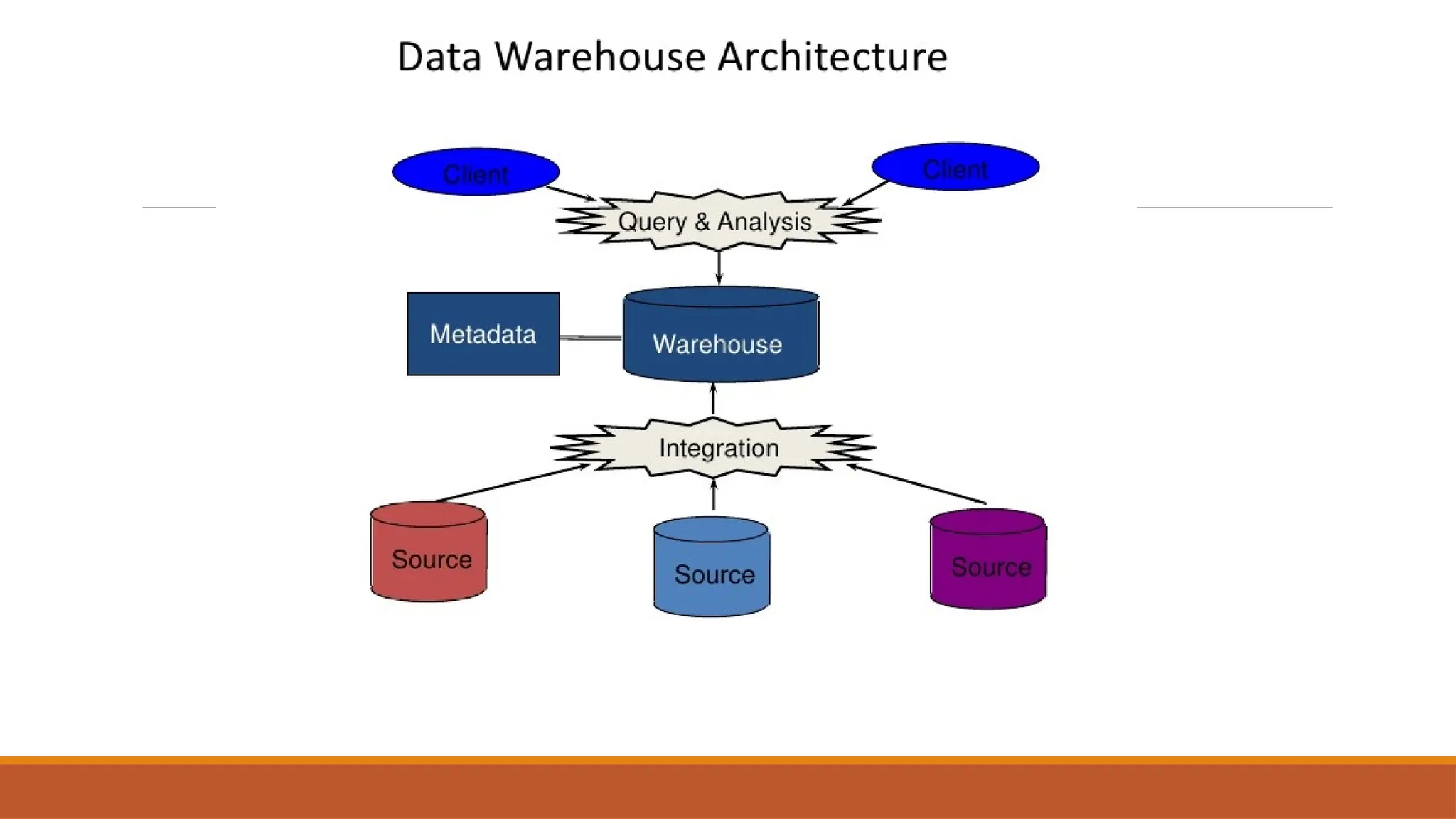
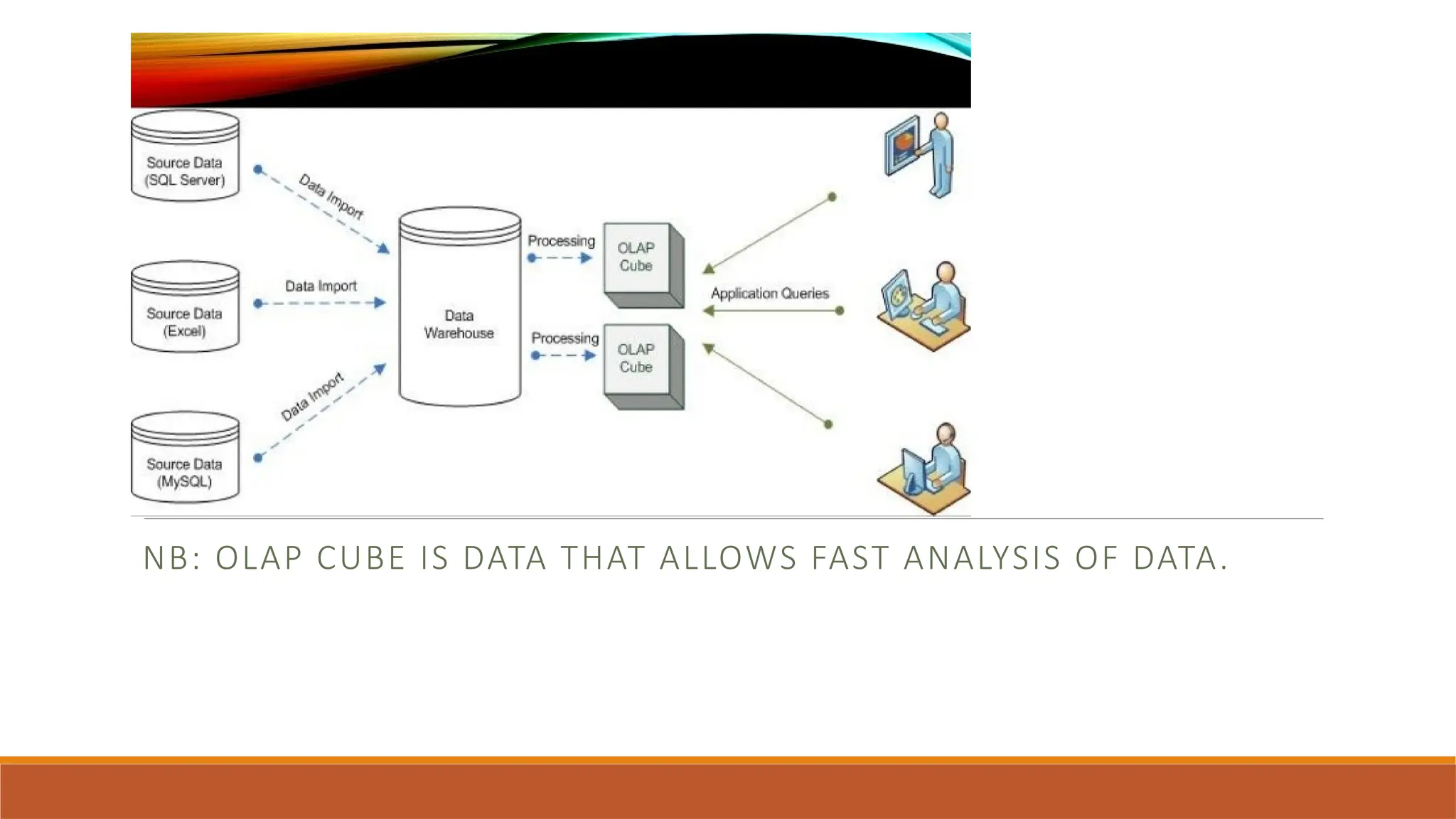
The document provides an overview of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), detailing its evolution, components, benefits, and related technologies like data warehousing, data mining, and OLAP. It highlights the importance of ERP in integrating business processes, enhancing decision-making, and improving operational efficiency. The document also discusses challenges and limitations of ERP systems while emphasizing the role of technologies like Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) in transforming and optimizing business operations.