This document provides information about genetics and inheritance from a grade 12 lesson. It discusses:
1. What genetics is and how it relates to heredity and similarities/differences between parents and offspring.
2. Gregory Mendel's pioneering genetics experiments in the 1800s using pea plants which discovered the basic principles of heredity and inheritance through generations. He demonstrated dominant and recessive traits and that genes exist in different alleles.
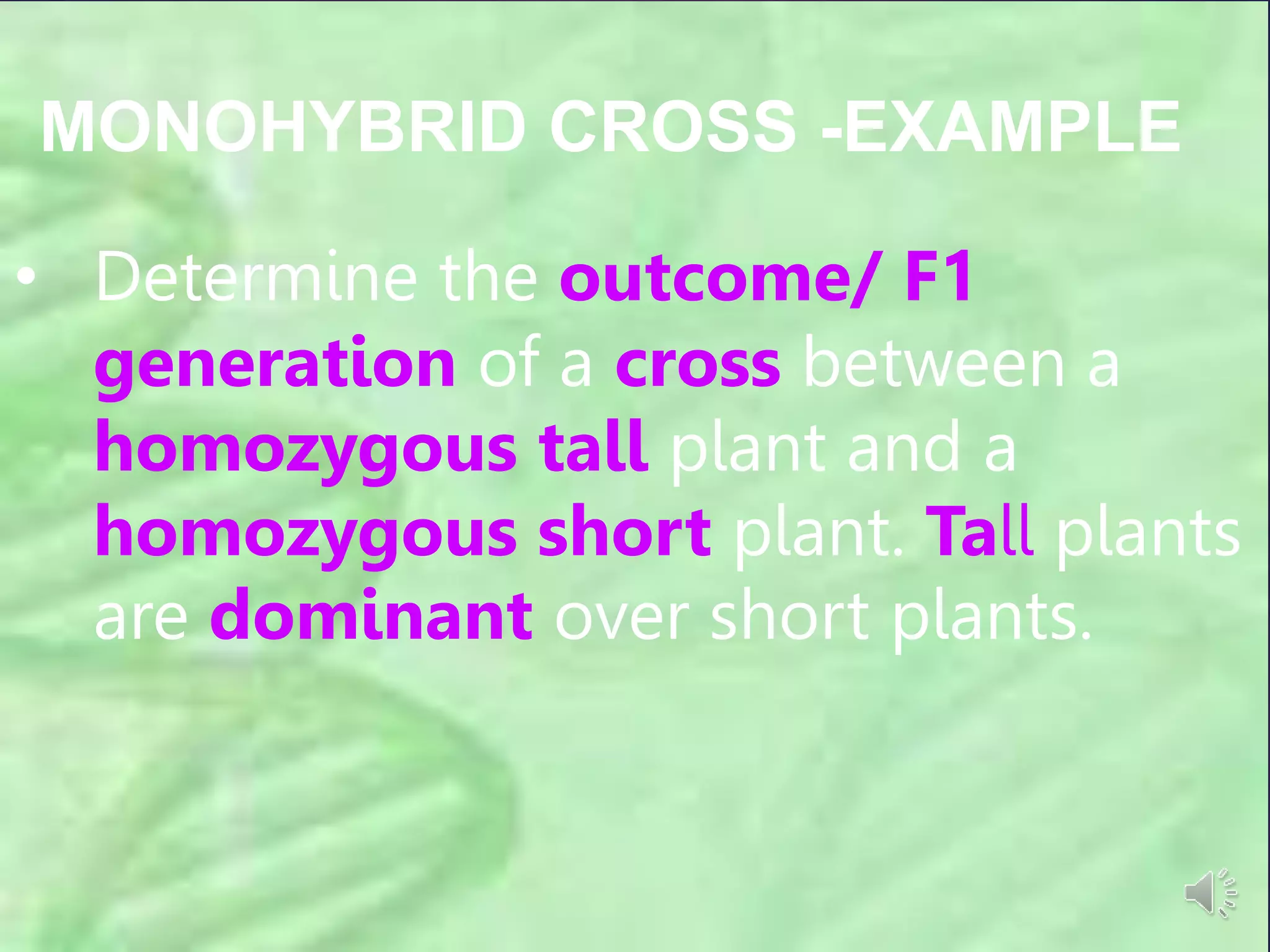
3. How to solve genetic cross problems by determining the genotypes and phenotypes of parents and predicting offspring based on dominant and recessive traits. It provides examples of monohybrid and dihybrid cross problems involving traits like plant height, eye color in rabbits, and seed shape