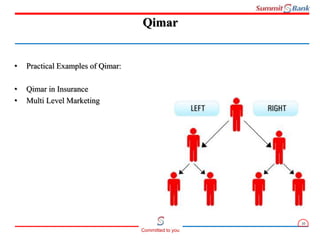
Gharar refers to uncertainty in the essential elements of a contract that makes the contract invalid according to Islamic law. There are several types of uncertainties that can cause Gharar, including uncertainty around the existence, possession, terms, subject matter, price, or time period. A contract with Gharar is not considered valid. Qimar refers to a contract where parties risk their wealth based on an uncertain outcome, with the possibility of one party gaining the other's wealth for nothing or losing their own wealth for nothing. For a contract to be considered Qimar, it must involve risking wealth between two or more parties based on an uncertain event, with the possibility of gaining another's wealth without compensation or losing one's own wealth