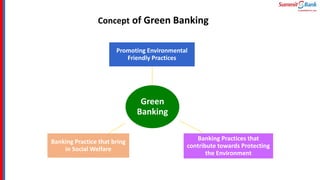
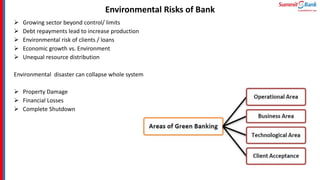
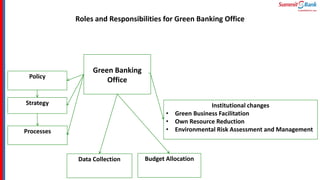
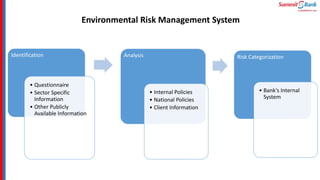
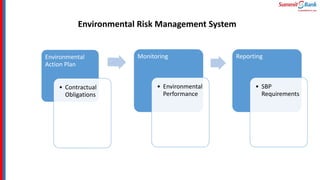
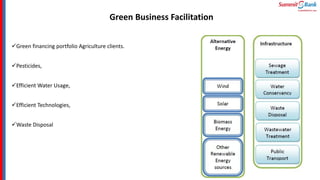
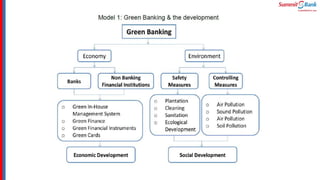
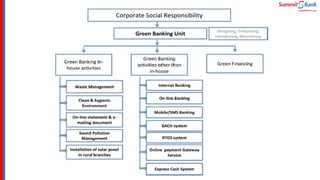
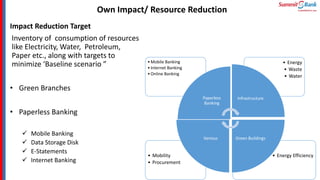
The document introduces green banking guidelines issued by the State Bank of Pakistan for banks and financial institutions. It outlines the regulatory requirements for green banking, including developing environmental risk management procedures and reducing environmental impacts from banks' own operations. It then discusses key concepts of green banking like environmental risk assessment, green business facilitation, and reducing banks' own environmental impact. The roles and responsibilities of different departments in implementing green banking strategies are also covered.