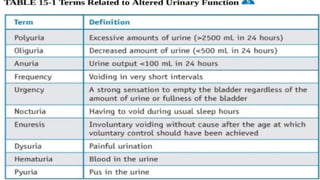
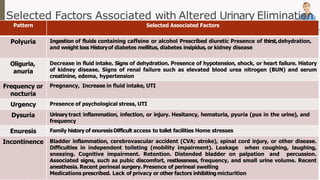
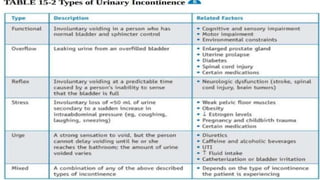
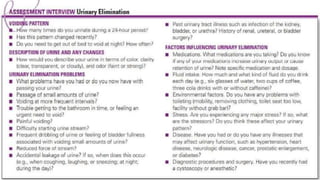
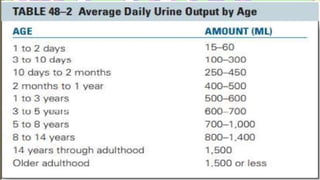
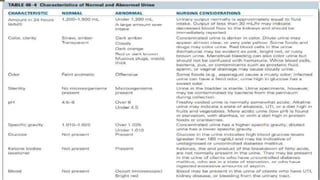
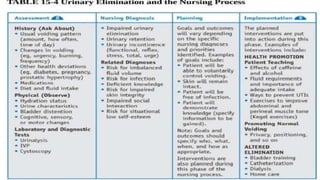
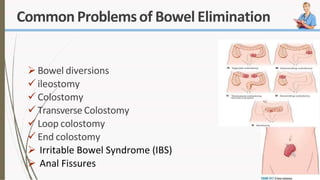
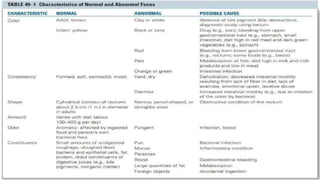
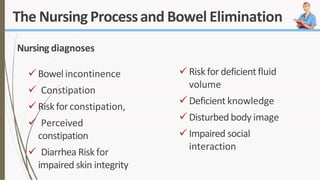
The document discusses the concept of elimination, defining it as the process of discharging waste from the body through urinary and bowel systems. It details urinary and bowel elimination patterns, factors affecting them, common problems, and nursing assessments and interventions related to elimination issues. Key issues include urinary retention, incontinence, UTIs, and bowel disorders, emphasizing the significance of individualized care based on various influencing factors.