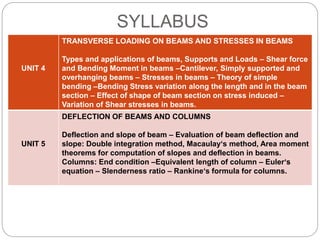
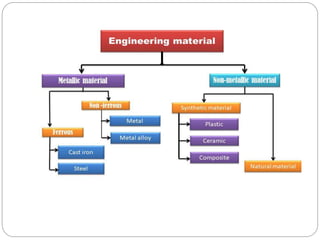
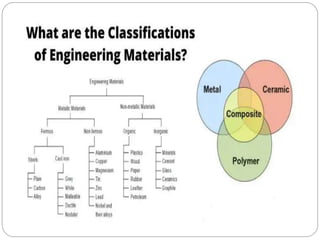
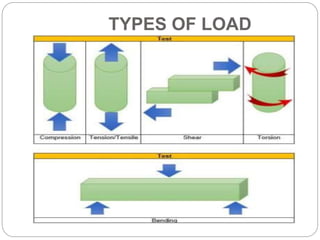
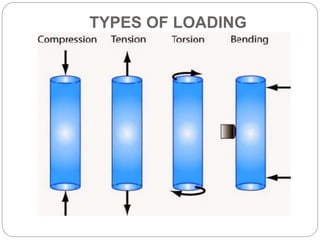
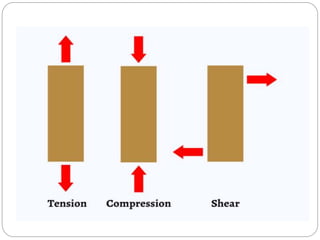
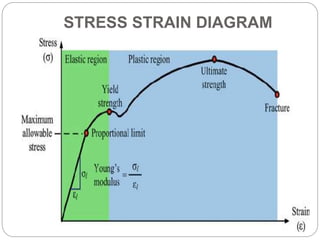
This document outlines the syllabus for a Strength of Materials course. The syllabus covers 5 units: 1) stress, strain and deformation of solids; 2) torsion and springs; 3) analysis of stresses in two dimensions; 4) transverse loading on beams and stresses in beams; and 5) deflection of beams and columns. Key concepts covered include stresses and types of stresses, elasticity, stress-strain diagrams, shear force and bending moment in beams, beam deflection analysis methods, and column buckling.