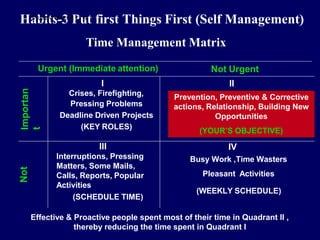
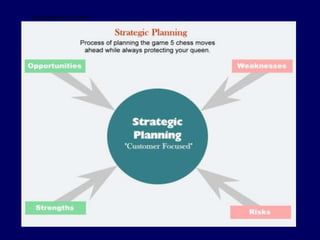
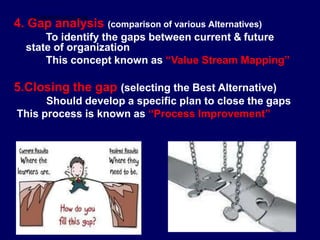
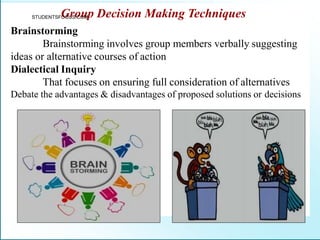
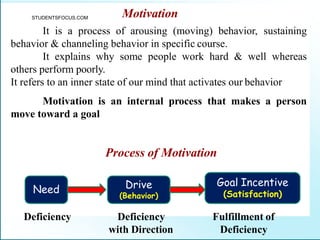
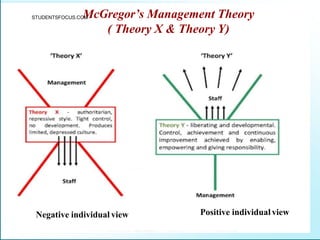
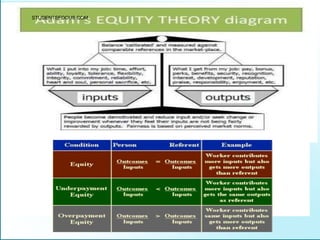
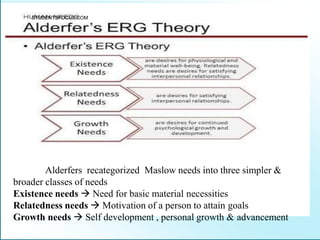
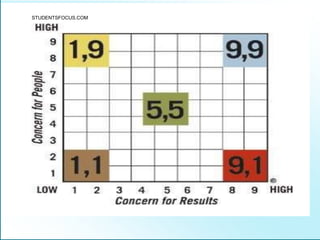
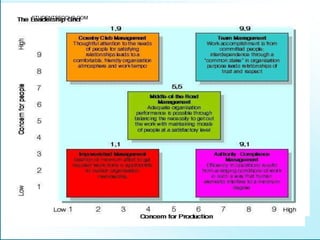
Leadership is defined as influencing others towards achieving goals. It involves guiding followers through both direction and inspiration. Effective leadership requires knowledge, skills, and motivation. Key leadership qualities include communication skills, technical competence, self-confidence, and the ability to build morale and coordinate teams. Leaders must empower subordinates, encourage continuous improvement, and prevent problems through training and guidance rather than direct supervision. Strategic planning sets long-term goals and objectives to guide an organization towards its vision of the future.