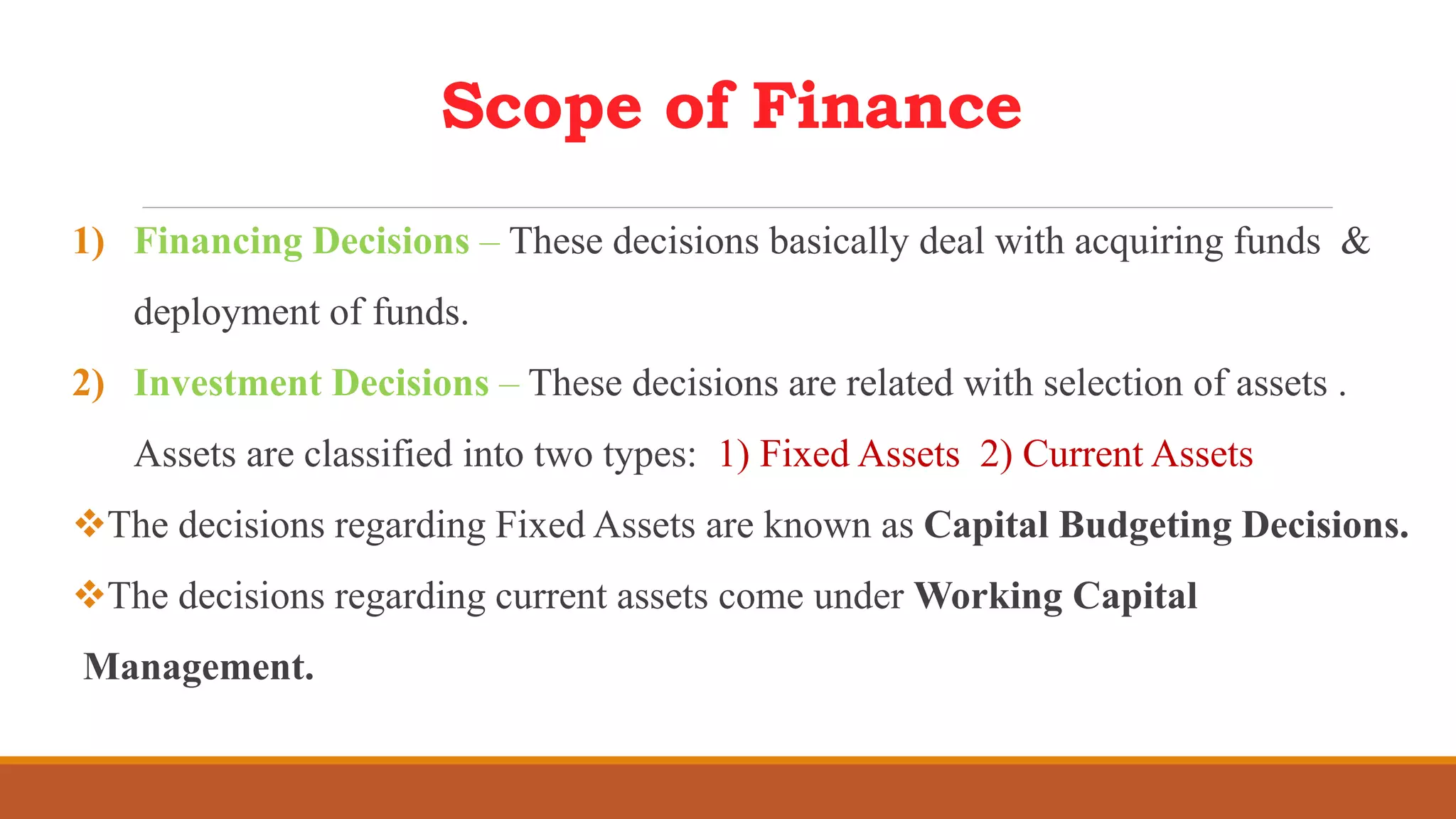
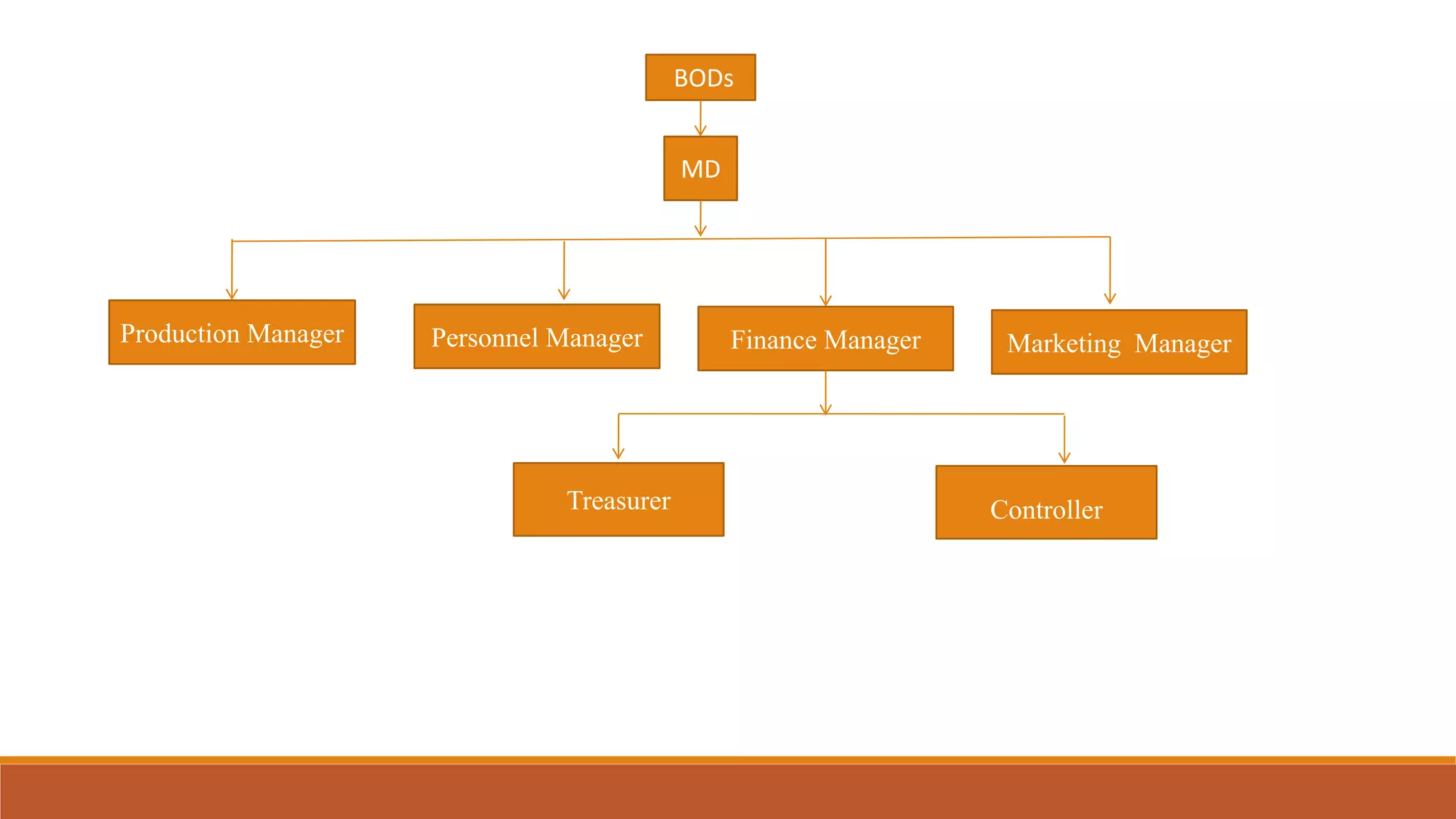
This document outlines the syllabus for an introduction to finance course. The syllabus covers topics such as the time value of money, valuation of bonds and shares, sources of long-term finance, raising long-term finance, and management of cash and receivables. It also defines financial management and discusses the objectives, scope, and functions of the finance department as well as the roles of the treasurer and controller.