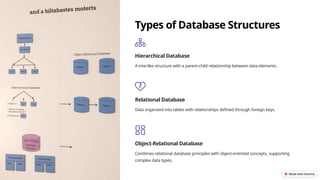
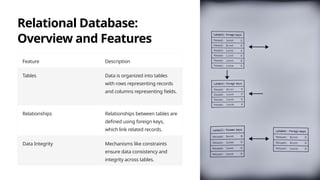
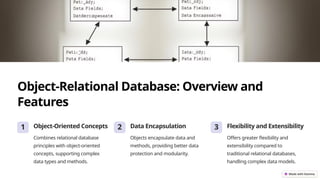
This document introduces various types of files and databases, focusing on flat files and their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. It also describes database structures, including hierarchical, relational, and object-relational databases, outlining their features and benefits for data management. The comparison emphasizes how databases allow for organized data, relationships, and stronger data integrity compared to flat files.