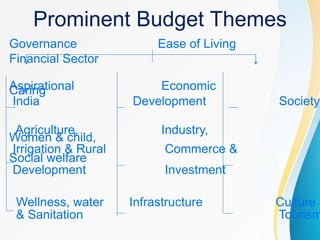
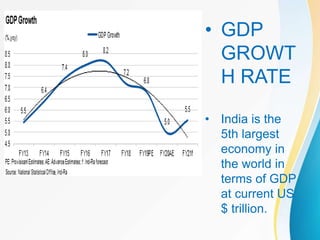
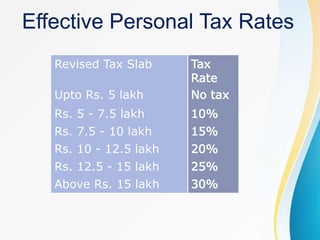
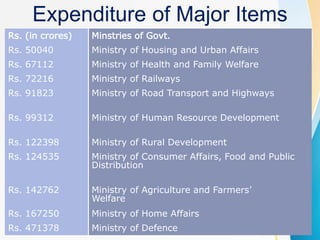
The document summarizes the key aspects of the Union Budget 2020-21 presented by the Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, including structural reforms focused on governance, financial sector, agriculture, and infrastructure development, as well as expenditure estimates and tax proposals aimed at boosting the Indian economy and achieving the government's vision of an aspirational India. The budget aims to balance growth promotion with fiscal discipline through measured stimulus targeted at entrepreneurship, trust-building, and citizen prosperity.