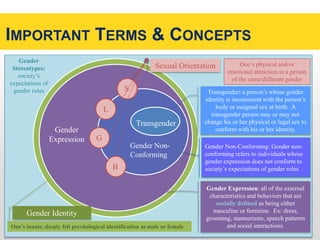
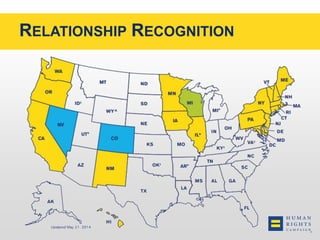
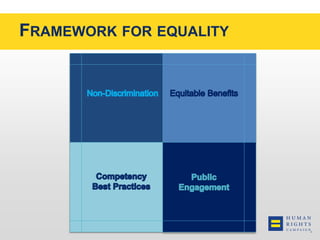
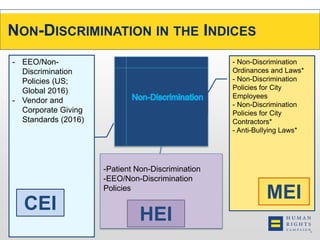
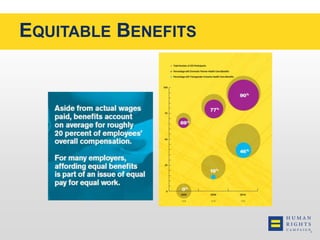
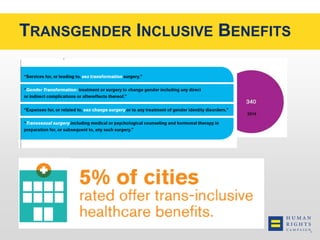
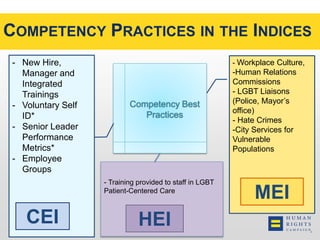
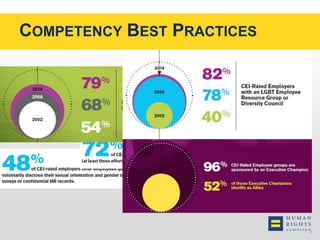
This document discusses the Human Rights Campaign's Corporate Equality Index, Municipal Equality Index, and Healthcare Equality Index which evaluate LGBTQ inclusion and equality. It covers important terms related to gender and sexual orientation. It also discusses the indices' focus on non-discrimination policies, equitable benefits for employees, competency training, and public engagement efforts. The indices are presented as tools to help institutions advance inclusion and overcome legal and social challenges to equality.