Recommended
PDF
PPT
PPT
Relation Slides.ppt data structure slides for explained process
PPT
FIRST TOPIC (RELATION AND FUNCTION).ppt general mathematics
PPTX
RELATIONS_AND_FUNCTIONS.pptx
PDF
relationsandfunctionslessonproper-160929053921.pdf
PPT
relationsandfunctionslessonproper-160929053921.ppt
PDF
relationsandfunctionslessonproper-160929053921.pdf
PPT
relationsandfunctionslessonproper-160929053921.ppt
PPTX
relationsandfunctions-for the students.pptx
PPT
relationsandfunctionslessonproper-160929053921.ppt
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
General Mathematics Lesson 1 on Functions and relation.pptx
PPTX
Lesson 1 functions as models
PPT
relationsandfunctionsupdated-140102120840-phpapp01.ppt
PPTX
Relations & Functions.pptx
PPT
L1_Functions_and_Relations.ppt
PPT
L1_Functions_and_Relations in mathematics
PPT
L1_Functions_and_Relations.ppt
PPT
L1_Functions_and_Relations.ppt
PPTX
L1_Functions_and_Relations.pptx
PPTX
Mathematics 8 relations and functions.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Functions and it's graph6519105021465481791.pptx
PPT
Relations and Functionsdnnfqfqfffwgwfacsrg
PPTX
ENGLISH-7-Quarter-4-Week-3 Matatag .pptx
PPTX
How to Track Employee Skill Growth with Skills Evolution Report in Odoo 18
More Related Content
PDF
PPT
PPT
Relation Slides.ppt data structure slides for explained process
PPT
FIRST TOPIC (RELATION AND FUNCTION).ppt general mathematics
PPTX
RELATIONS_AND_FUNCTIONS.pptx
PDF
relationsandfunctionslessonproper-160929053921.pdf
PPT
relationsandfunctionslessonproper-160929053921.ppt
PDF
relationsandfunctionslessonproper-160929053921.pdf
Similar to UNDERSTANDING RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS...
PPT
relationsandfunctionslessonproper-160929053921.ppt
PPTX
relationsandfunctions-for the students.pptx
PPT
relationsandfunctionslessonproper-160929053921.ppt
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
General Mathematics Lesson 1 on Functions and relation.pptx
PPTX
Lesson 1 functions as models
PPT
relationsandfunctionsupdated-140102120840-phpapp01.ppt
PPTX
Relations & Functions.pptx
PPT
L1_Functions_and_Relations.ppt
PPT
L1_Functions_and_Relations in mathematics
PPT
L1_Functions_and_Relations.ppt
PPT
L1_Functions_and_Relations.ppt
PPTX
L1_Functions_and_Relations.pptx
PPTX
Mathematics 8 relations and functions.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Functions and it's graph6519105021465481791.pptx
PPT
Relations and Functionsdnnfqfqfffwgwfacsrg
Recently uploaded
PPTX
ENGLISH-7-Quarter-4-Week-3 Matatag .pptx
PPTX
How to Track Employee Skill Growth with Skills Evolution Report in Odoo 18
PDF
TỔNG HỢP 156 ĐỀ CHÍNH THỨC KỲ THI CHỌN HỌC SINH GIỎI TIẾNG ANH LỚP 12 CÁC TỈN...
PDF
Judgement Regarding Land Acquisition Act not Applicable to Encroachers.pdf
PPTX
EYE IRRIGATION AND INSTILLATION....pptx
PPTX
Saber tooth tiger.pptx (Smilodon presentation ) = Extinct Animals
PPTX
Chapter 1 - Introduction to Business Research.pptx
PDF
operation with integers and finding common ground worksheet solutions/7th cla...
PDF
Pratishta Educational Society., Courses & Opportunities
PDF
Types of Foot & Foot Modifications in Birds
PPTX
Guidelines for reporting social networks and personal networks data
PDF
Unit Plan and Unit Test-pdf-Dr. Rajashekhar Shirvalkar, Principal, SMRS B.Ed ...
PDF
Why Projects Fail – The Need to “Do the Right Project” and “Do the Project Ri...
PDF
Chapter 05 Drugs Acting on the Central Nervous System: Anti-Depressant Drugs
PPTX
How Physician Assistants in the USA Earn CME Credits Online.pptx
PDF
RAJAT ARORA SIR PHYSICAL EDUCATION NOTES ALL CHAPTERS .pdf
PPTX
How to Easily Track Appraisal Analysis Report in Odoo 18 Appraisal
PDF
Project Management Unit I SE OE-II SPPU Pune (2024 Pattern)
PPTX
A detailed notes on Conjugate Vaccine and its mechanism.
PDF
PPT Daftar Bahan Kelas Bedah Kitab Matius Khotbah di Bukit
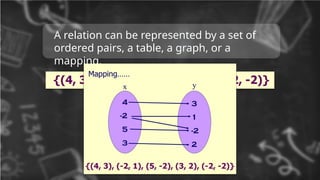
UNDERSTANDING RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS... 1. 2. A relation can be represented by a set of
ordered pairs, a table, a graph, or a
mapping.
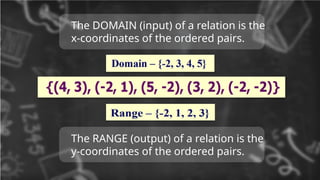
3. The DOMAIN (input) of a relation is the
x-coordinates of the ordered pairs.
The RANGE (output) of a relation is the
y-coordinates of the ordered pairs.
4. The INVERSE of a relation is found by
switching the coordinates of each
ordered pair.
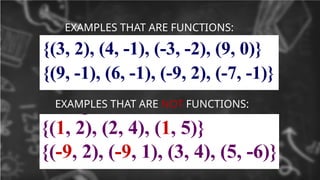
5. FUNCTIONS
a relation when each element of the domain is
paired with exactly one element of the range.
• For every x there is exactly one y.
• The x-coordinate cannot repeat.
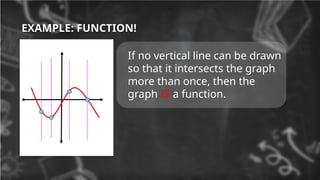
6. 7. 8. EXAMPLE: FUNCTION!
If no vertical line can be drawn
so that it intersects the graph
more than once, then the
graph IS a function.
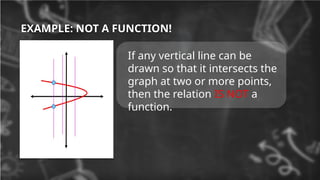
9. EXAMPLE: NOT A FUNCTION!
If any vertical line can be
drawn so that it intersects the
graph at two or more points,
then the relation IS NOT a
function.
10. 11. 12. 13.