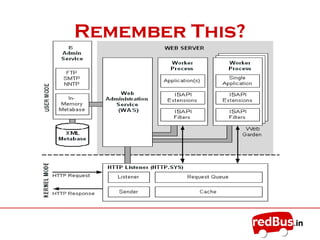
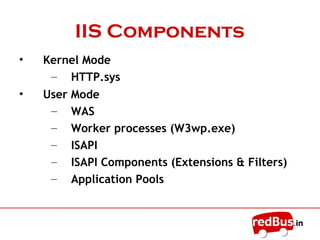
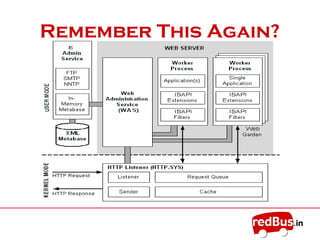
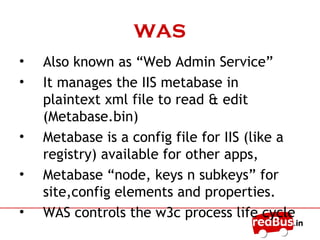
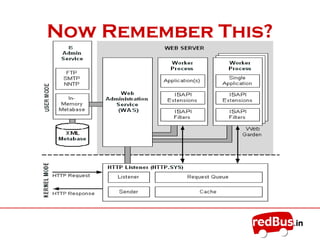
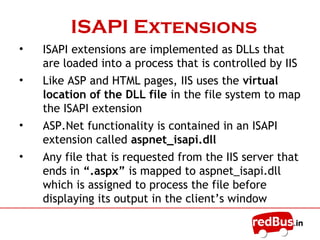
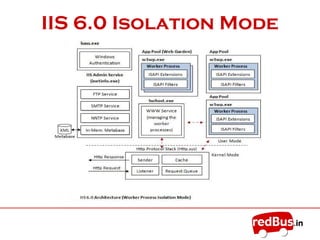
The document provides an overview of the key components of Internet Information Services (IIS). IIS fulfills the role of a web server by responding to requests for files and logging activity. It maintains information about content locations, security access, and URL mappings. The core components of IIS include HTTP.sys, the WWW service, worker processes (W3wp.exe), ISAPI extensions and filters, and application pools. HTTP.sys receives requests and passes them to worker processes. The WWW service manages the configuration and application pools. Worker processes execute application code and use ISAPI components to process requests and return responses.