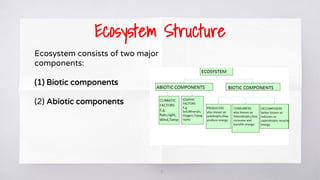
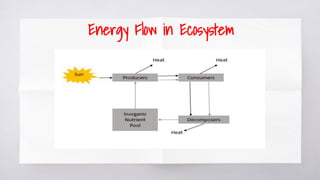
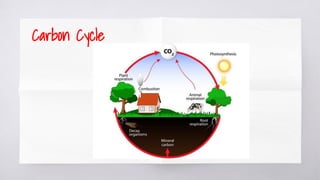
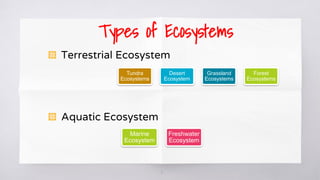
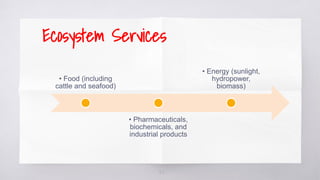
The document provides an overview of ecosystems, highlighting their biotic and abiotic components, and the flow of energy and chemical elements within them. It discusses various types of ecosystems, emphasizing terrestrial and aquatic environments, while detailing the negative impacts of human activities on ecosystems such as pollution and deforestation. The consequences of ecosystem destruction are outlined, highlighting issues like climate change, food shortages, loss of biodiversity, and the importance of preserving ecosystems for sustaining life.