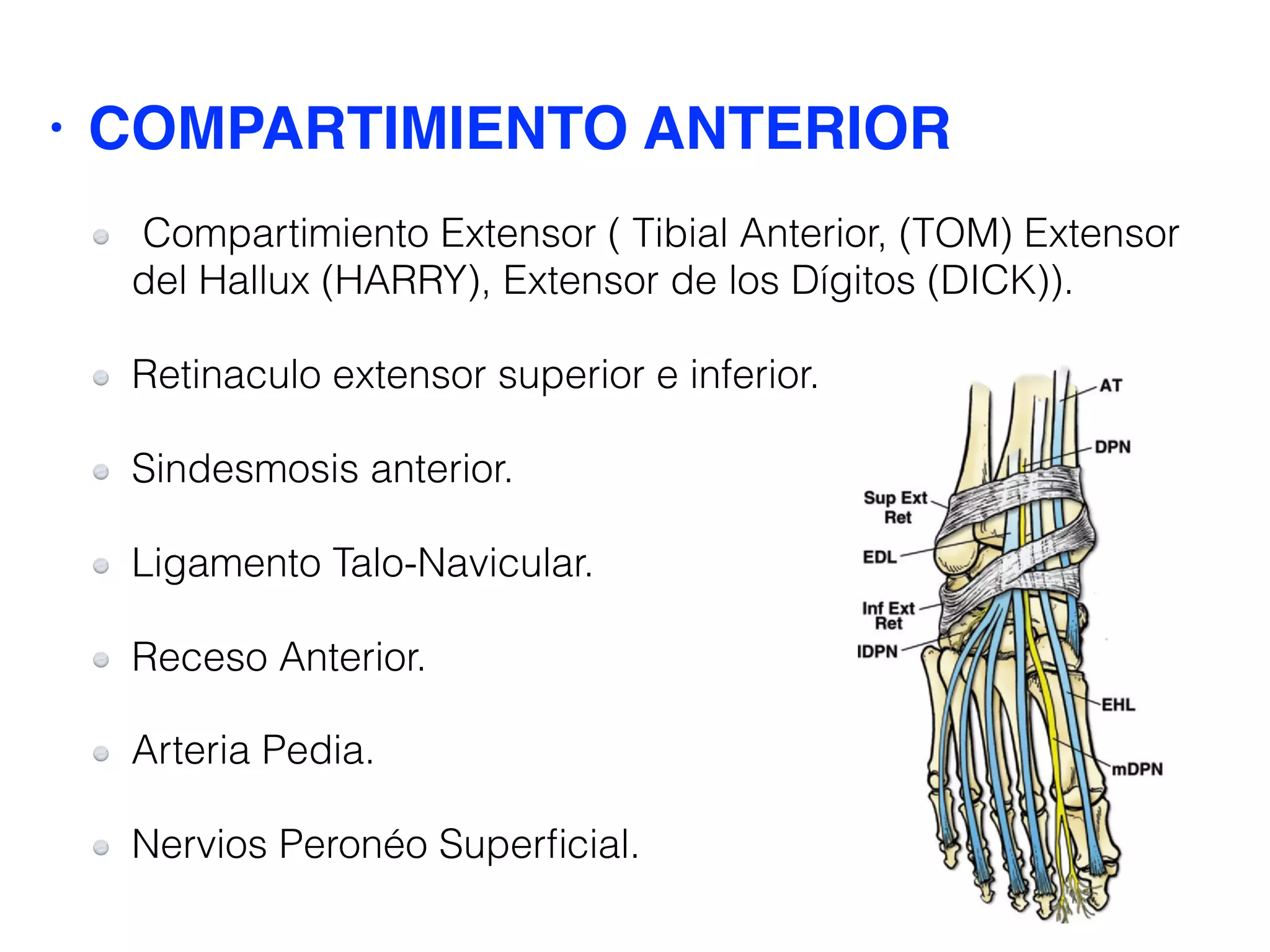
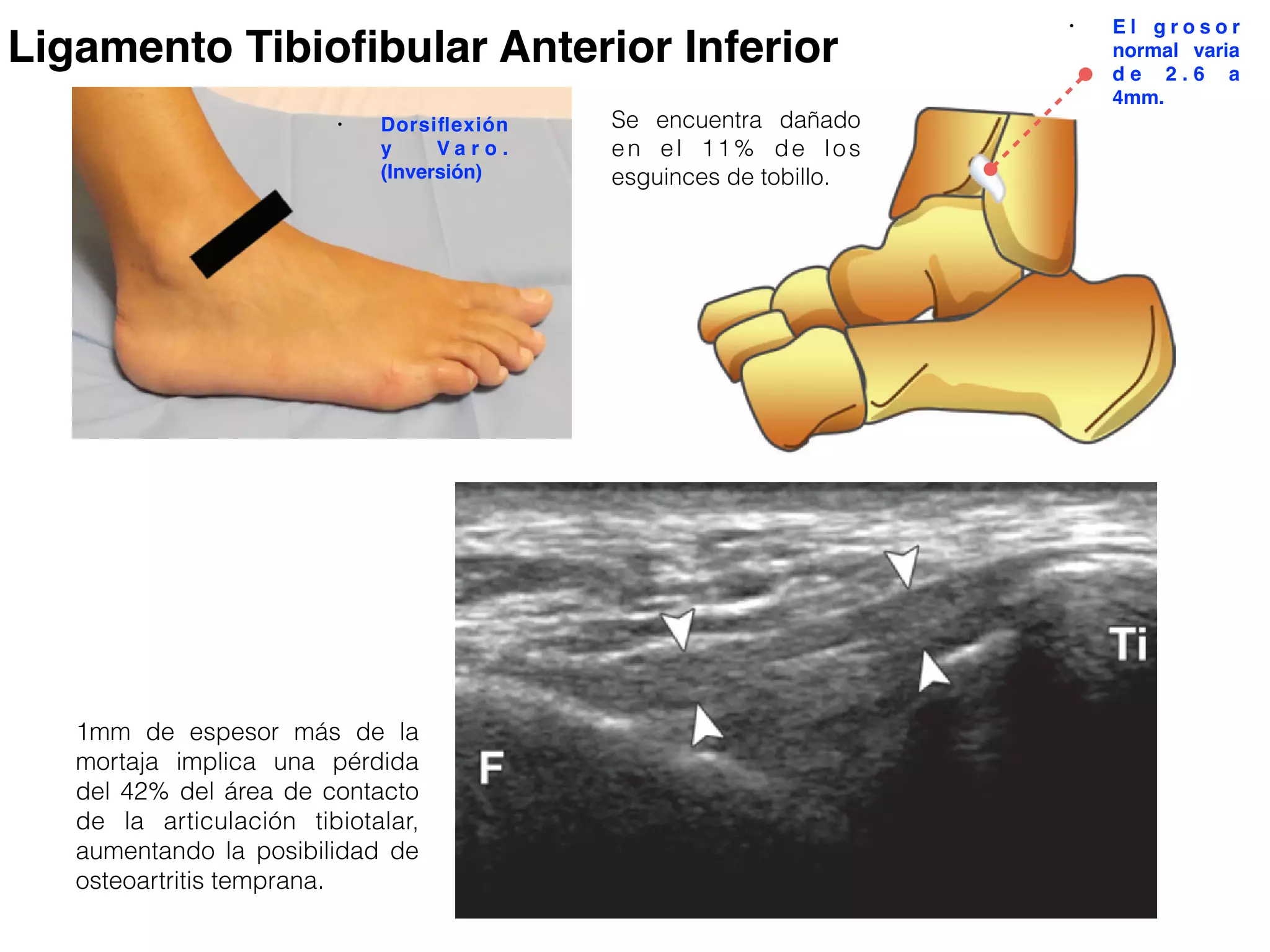
The document provides a detailed examination of the ankle joint, emphasizing the common injuries and the use of ultrasound (US) for diagnosis. It discusses the anatomy of the ankle ligaments, particularly focusing on the anterior talofibular and calcaneofibular ligaments, and outlines protocols for evaluating ligament injuries. The importance of early diagnosis to preserve function is highlighted, as well as techniques for image acquisition and assessment during ultrasound examination.




























![t parallel to the sole of the foot (Fig 4b).
nterior talofibular ligament can be seen as a
echoic fibrillar band in tension between the
l malleolus and the talus (Movie 2 [online]).
unctionality of the anterior talofibular liga-
can be tested by using the anterior drawer
This test consists of stressing the plantar
peroneus longus tendon.
Figure 8. US scan shows a partial tear of the CFL.
The ligament appears inhomogeneous and hy-
poechoic (arrowheads), with periligamentous effu-
sion (*). C = calcaneus, F = fibula, PBT = peroneus bre-
vis tendon, PLT = peroneus longus tendon, Ta = talus.
originates from the lateral mal-
teral surface of the calcaneus.
anatomic structure. (b) Probe po-
US scan of the CFL (arrowheads).
peroneus brevis tendon, PLT =
Ligamento Calcáneofibular.
Flexión dorsal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ultrasonidodetobilloanatomia-160425211615/75/Ultrasonido-de-tobillo-anatomia-31-2048.jpg)

![Lesión parcial del CFL.
as a
the
e]).
a-
er
may
s
ent
of the probe should be held over the tip of the
lateral malleolus and the probe should be ro-
tated caudad to reach a coronal plane, with the
distal edge of the probe slightly posterior to
the CFL.
and hy-
us effu-
eus bre-
a = talus.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ultrasonidodetobilloanatomia-160425211615/75/Ultrasonido-de-tobillo-anatomia-33-2048.jpg)


























