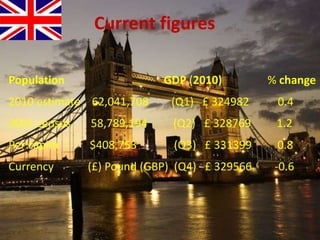
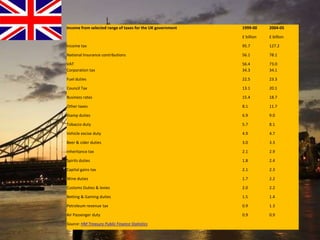
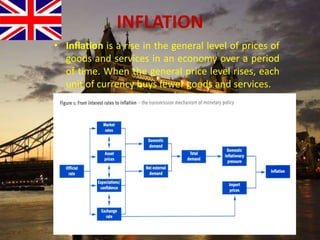
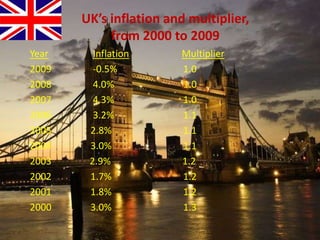
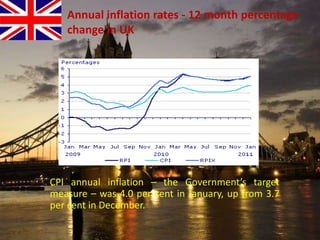
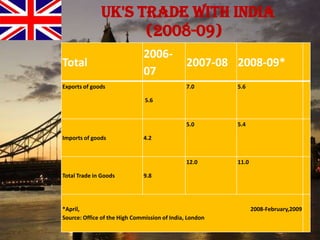
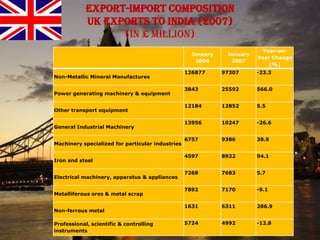
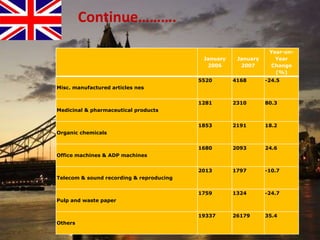
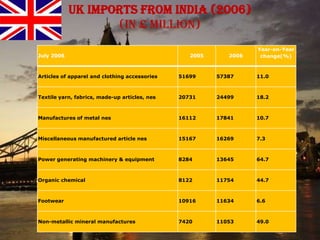
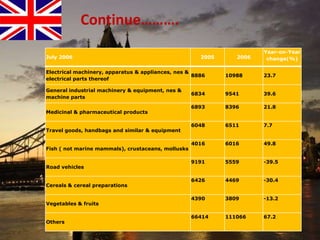
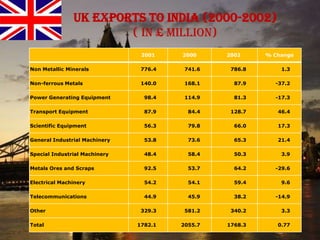
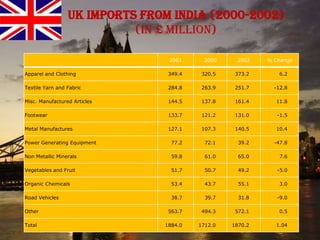
The document provides an overview of the United Kingdom's business environment and economy. It discusses key facts about the UK such as its population, GDP, currency, and status as a constitutional monarchy made up of four countries. It then summarizes sectors of the UK economy like manufacturing, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, fiscal and monetary policy, inflation rates from 2000-2009, recent recession from 2008-2009, and the UK's growing economic partnership with India.