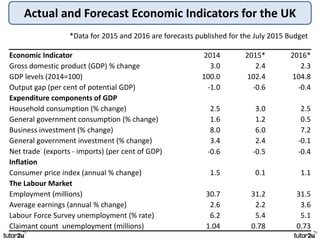
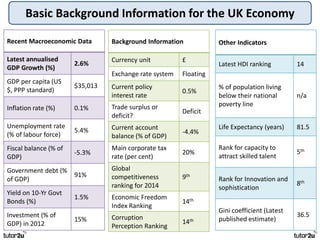
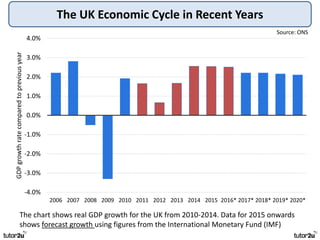
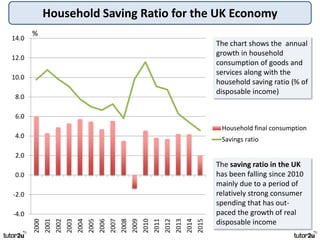
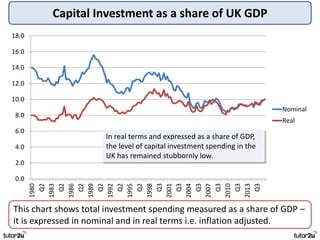
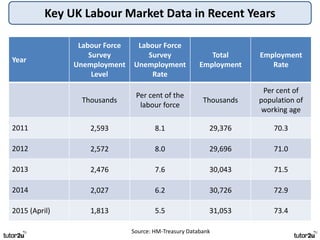
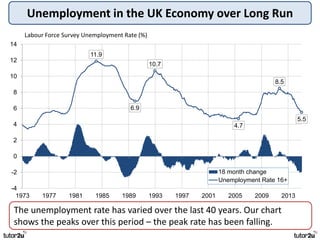
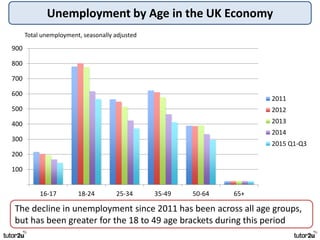
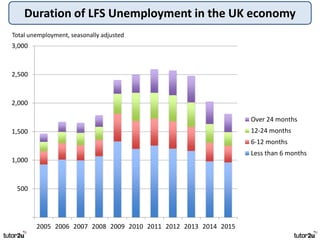
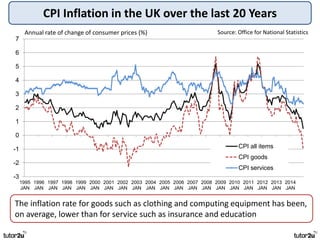
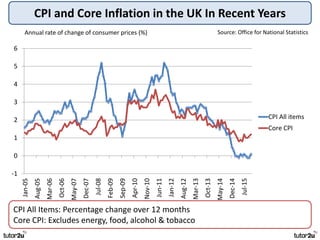
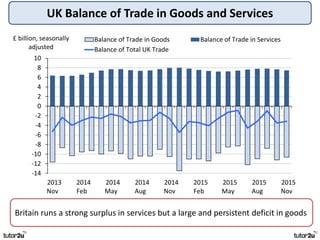
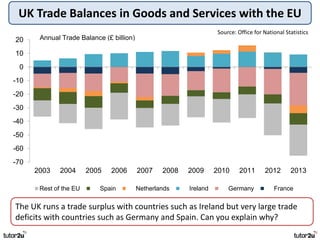
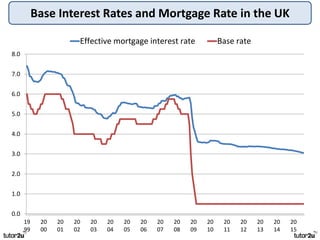
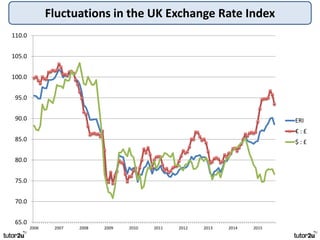
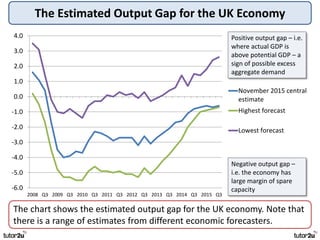
The key objectives of UK macroeconomic policy are price stability, economic growth, low unemployment, and higher living standards. Additional objectives include balancing the budget, improving well-being, regional balance, and access to services. Recent UK economic data shows GDP growth of 2.6% in 2014, inflation at 0.1%, unemployment at 5.4%, and a budget deficit of 5.3% of GDP. The UK runs trade deficits and has a floating exchange rate system.