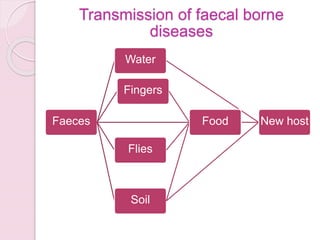
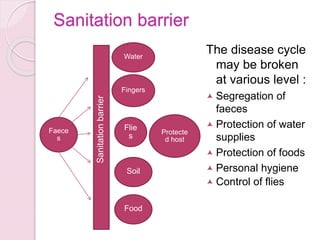
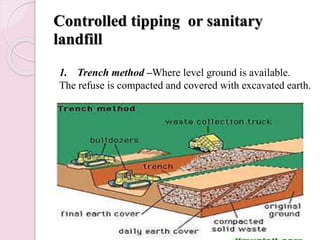
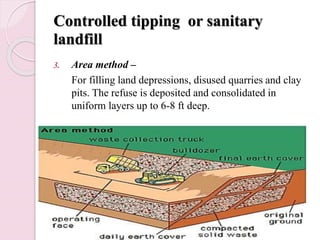
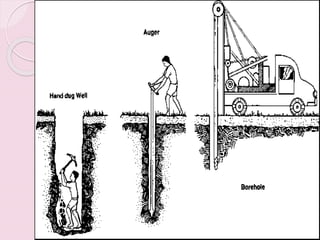
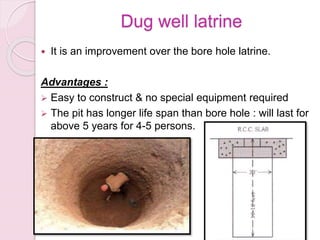
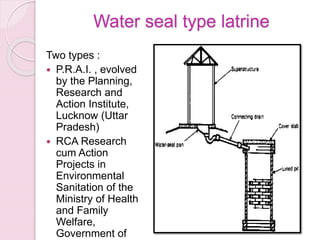
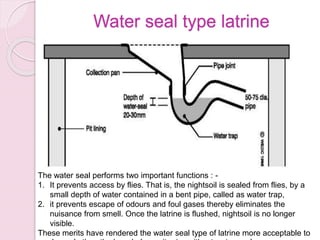
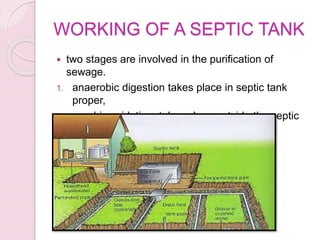
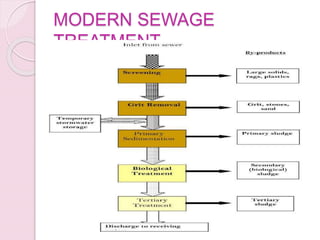
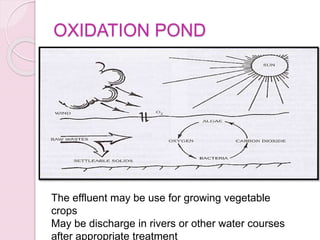
This document discusses proper disposal of waste and excreta, which are important for public health. It describes various types of waste that can cause health issues if improperly disposed. Methods of disposal for solid waste, refuse, sewage, and excreta are outlined, including dumping, controlled tipping, incineration, composting, and water carriage systems. Improper disposal can spread diseases through water, soil, food, and person-to-person contact. Proper sanitation and hygienic disposal methods like septic tanks, latrines, and sewage treatment are needed to protect public health.