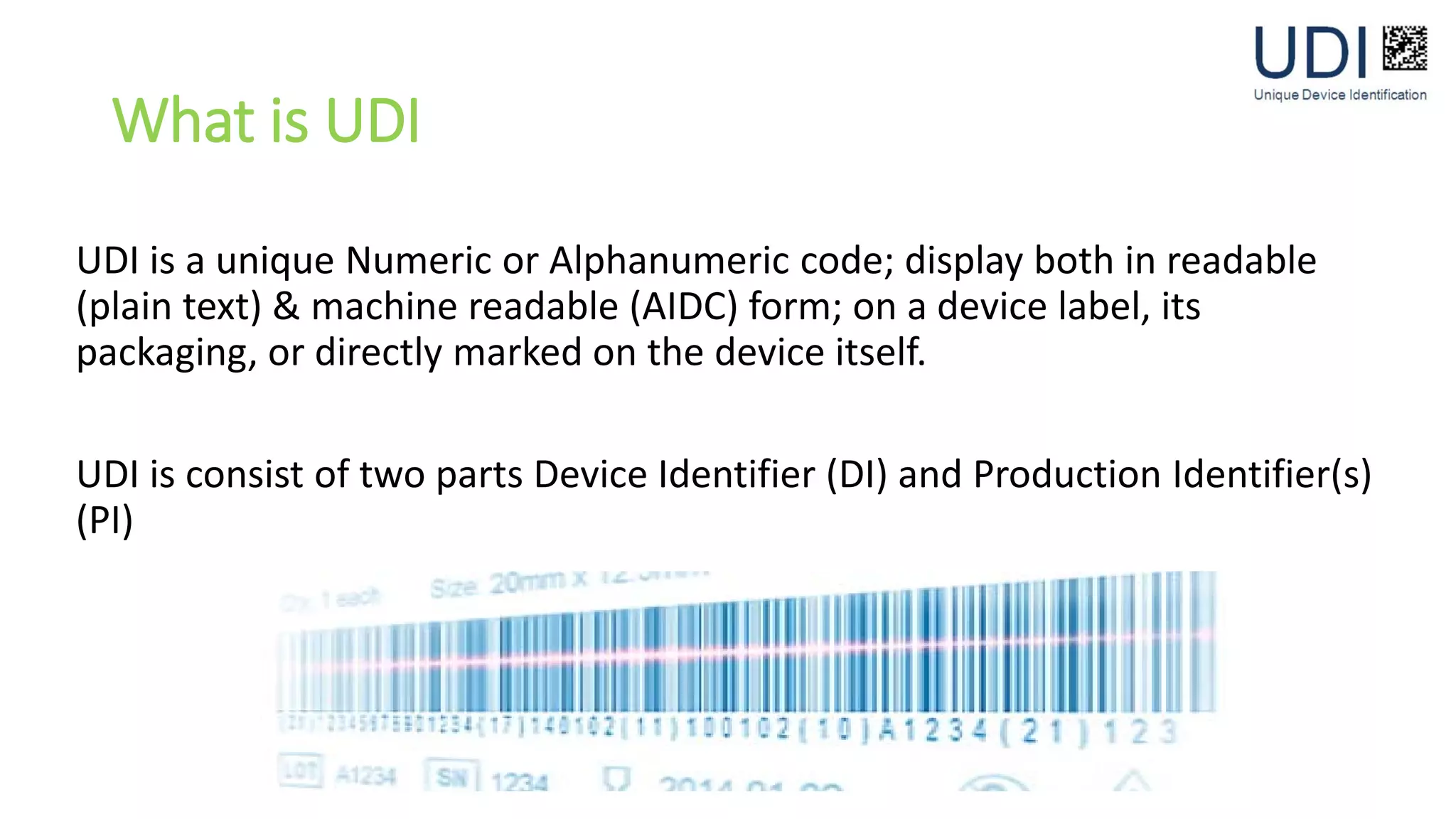
UDI consists of a unique device identifier (UDI) made up of a device identifier (DI) and production identifier(s) (PI). The DI is a static number assigned to each product model, while the PI contains variable information like serial number or lot number. UDI is displayed both visibly and in machine-readable form on medical devices and their packaging. Requiring UDI helps reduce medical errors, simplify data integration, and improve recall effectiveness. Exemptions may apply if direct marking could impact safety, performance, or additional processing is needed for single-use devices.