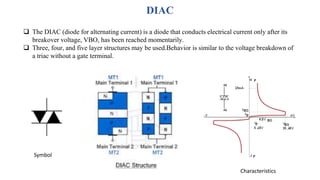
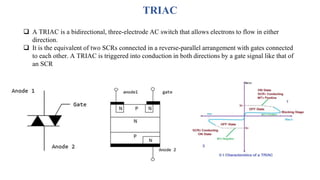
A thyristor is a four-layer semiconductor device made of alternating P-type and N-type materials that regulates current flow. The most common type is a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR), which has three electrodes - anode, cathode, and gate - and conducts current when a gate pulse is applied. An SCR is mainly used to control high voltage/power applications like motor control. It has four semiconductor layers arranged as NPNP or PNPN and three junctions. A DIAC is a diode that only conducts after reaching its breakover voltage, while a TRIAC is a bidirectional AC switch made of two reverse SCRs with connected gates.