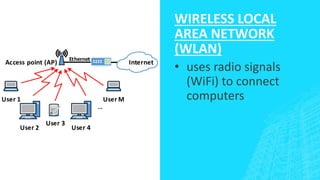
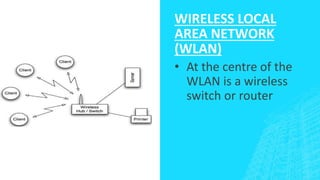
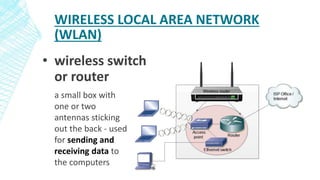
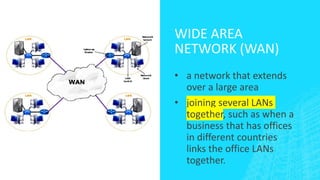
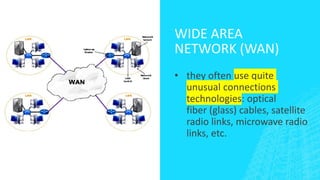
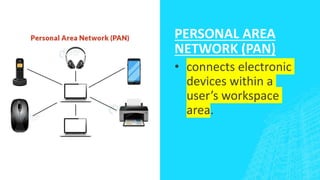
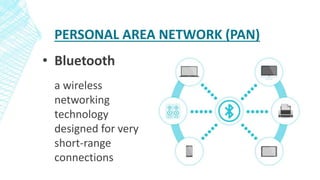
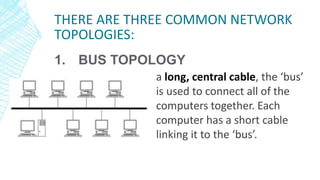
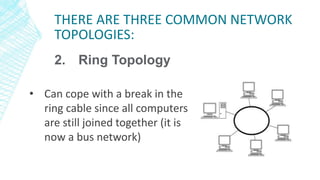
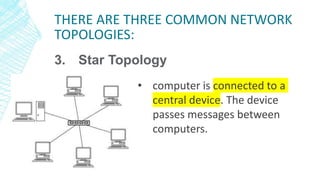
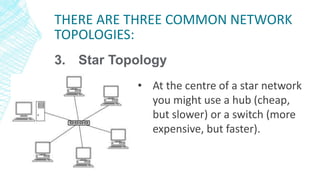
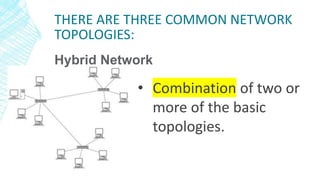
The document outlines four types of networks: Local Area Network (LAN), Wide Area Network (WAN), and Personal Area Network (PAN), each with distinct connection methods and uses. It also explains three common network topologies—bus, ring, and star—highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it mentions hybrid networks as combinations of different topologies.