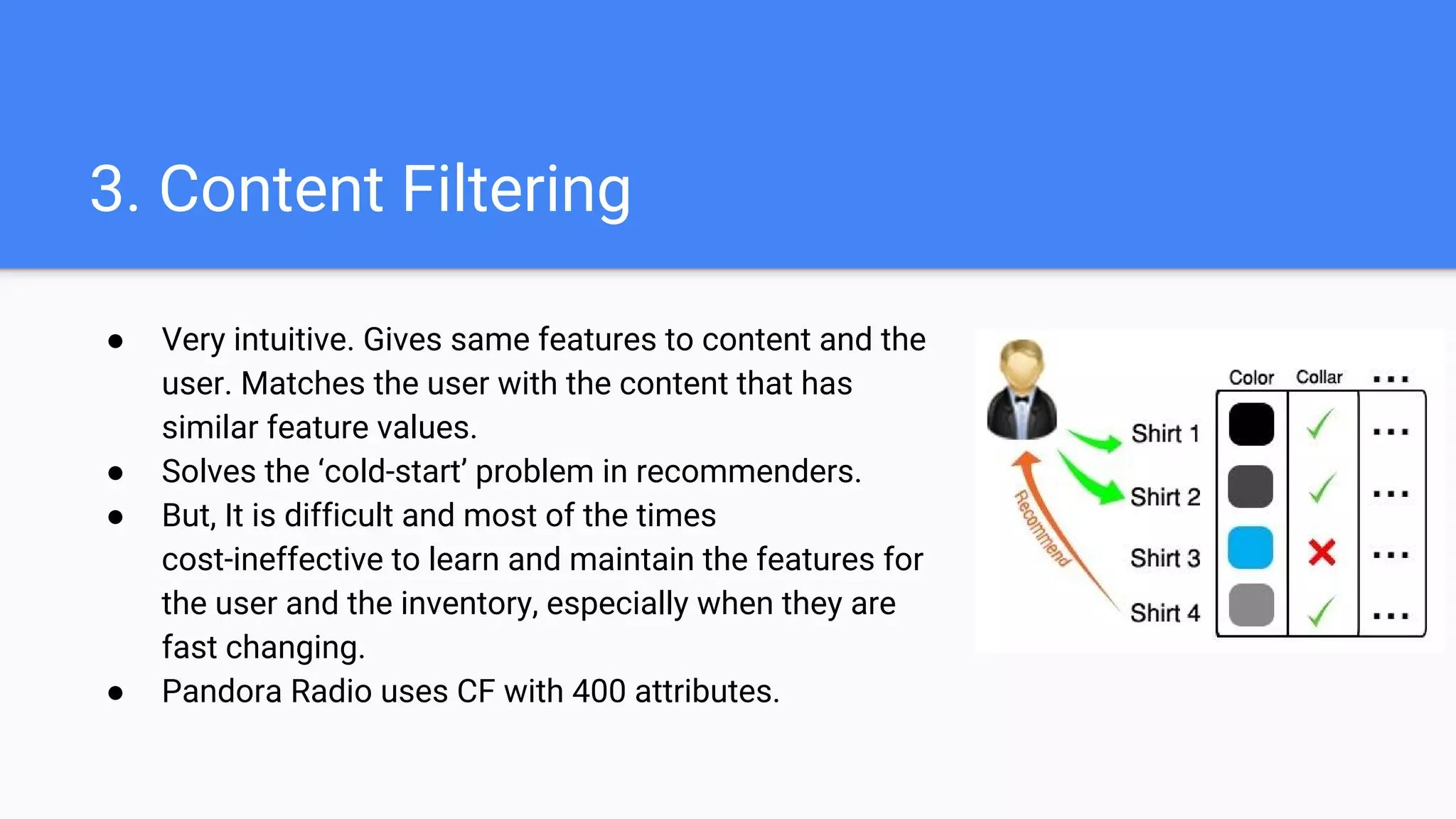
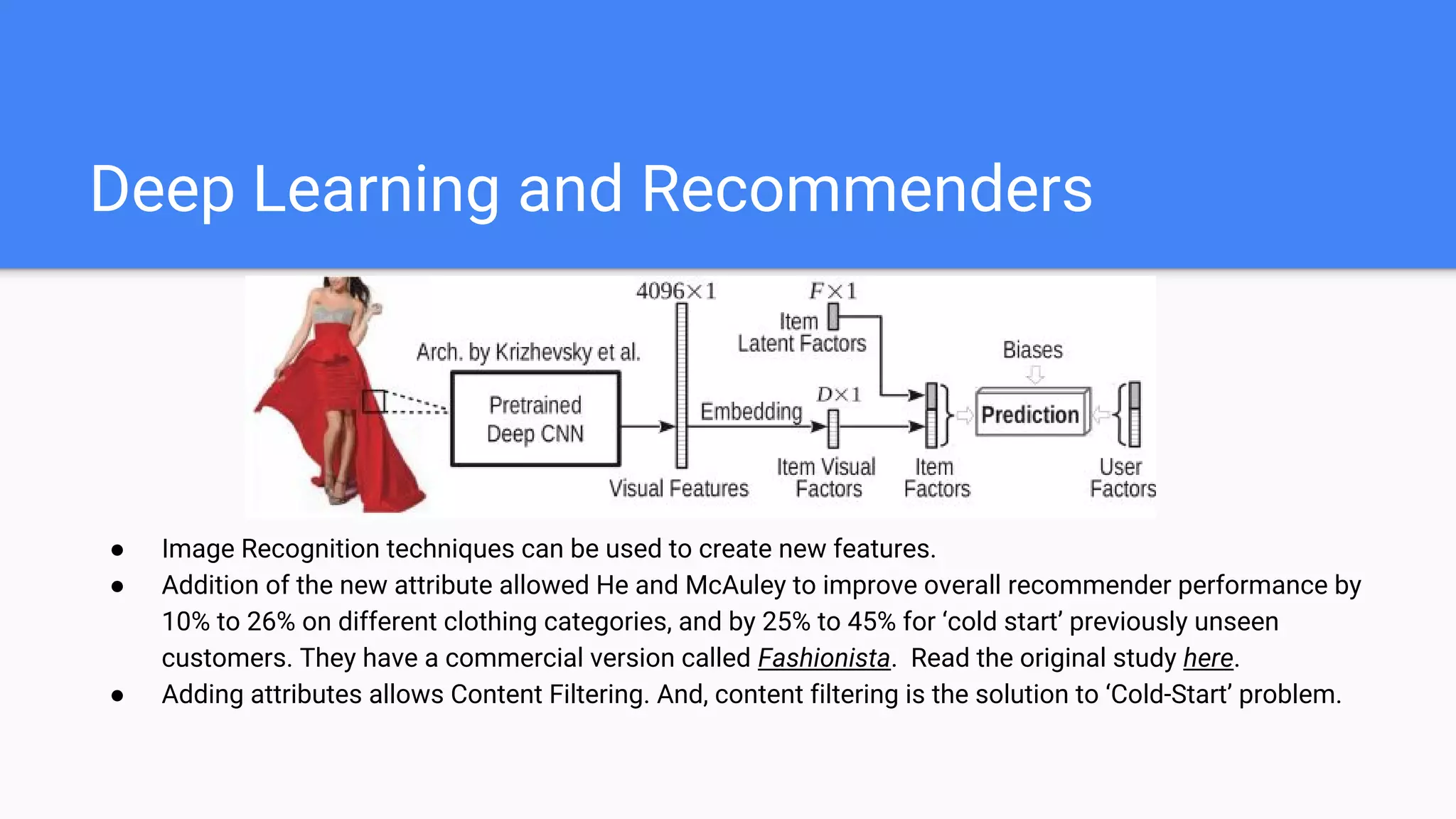
The document discusses various types of recommender systems, outlining their purposes, environments, and complexities. It describes five types of recommenders: most popular item, association/market basket analysis, content filtering, collaborative filtering, and hybrid models, each with unique strengths and limitations. Additionally, it addresses the potential of deep learning techniques to enhance recommender performance, particularly in solving the 'cold-start' problem.