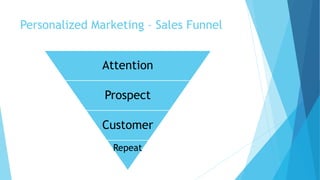
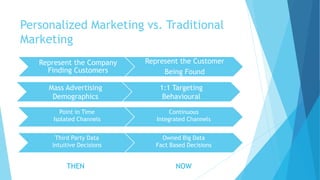
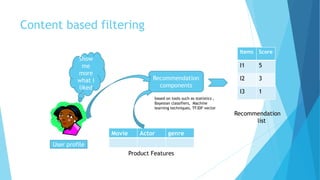
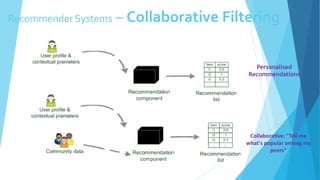
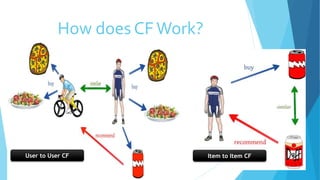
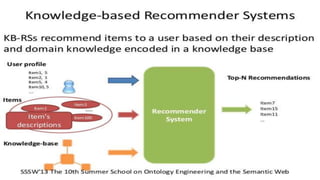
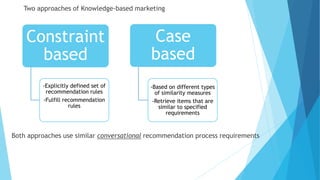
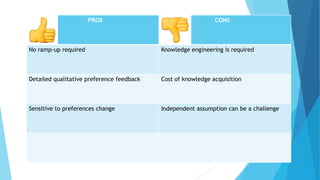
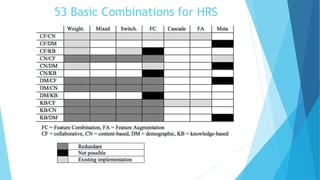
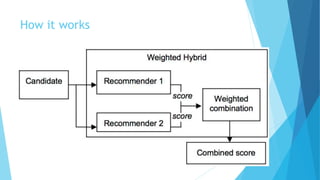
Personalized marketing creates individualized messages for consumers by using automated processes and customer-centric recommendation engines. It allows customers to customize products to their specifications. By offering consumers products they already want, businesses are more likely to convert visits to sales. Personalized marketing represents customers by finding them through their behavior and integrated channels, using owned big data and fact-based decisions. Recommender systems seek to predict user preferences and provide recommendations for items similar to a user's profile or items liked by similar users. Content-based filtering uses a user's profile while collaborative filtering matches users with similar tastes. Knowledge-based systems use defined rules or similarity measures to meet user requirements. Hybrid systems combine approaches to solve cold start problems and better adapt to changing