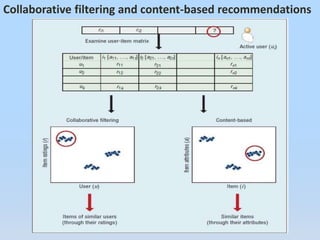
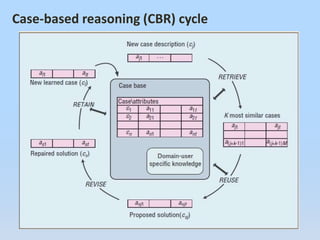
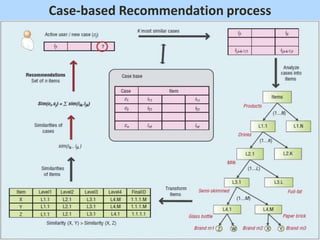
The document presents a case-based recommendation approach for market basket data, focusing on enhancing the effectiveness of recommendation systems for both users and providers. It explores various methodologies, including collaborative filtering and content-based recommendations, and highlights the advantages of case-based reasoning in addressing user preferences while acknowledging its limitations. Future work aims to incorporate quality characteristics of items and expand the application of this approach to other domains.