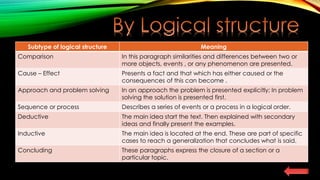
This document discusses different types of paragraphs based on their content, logical structure, and location. It identifies argumentative, definition, chronological, enumerative, descriptive, explicative, expository, and narrative paragraphs based on their content. Based on logical structure, it discusses comparison, cause-effect, approach and problem solving, sequence or process, deductive, and inductive paragraphs. Finally, it identifies opening, transition, and closing paragraphs based on their location within a text.