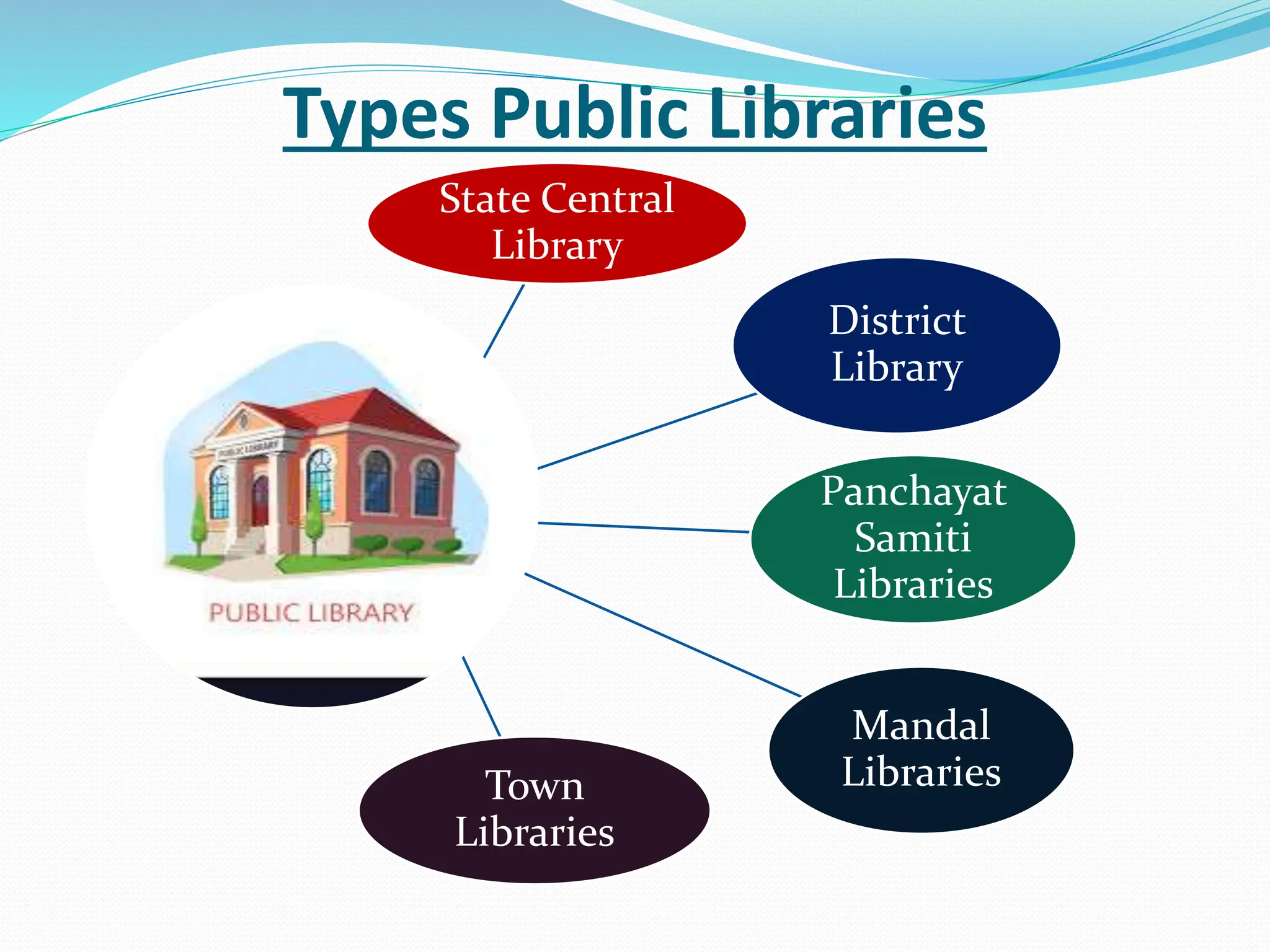
The document discusses various types of libraries in India, including national, public, special, and academic libraries, outlining their roles, functions, and services. It highlights the National Library of India as a key depository for cultural and bibliographic resources, while detailing the importance of public libraries in serving the community. Additionally, it describes the specific purposes and operations of various academic libraries, emphasizing their contributions to education and self-learning.