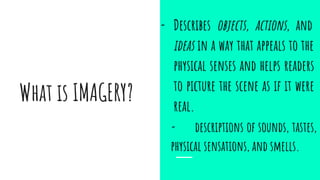
This document defines imagery and describes the five main types: visual, olfactory, gustatory, tactile, and auditory. Visual imagery involves descriptions that appeal to sight, olfactory imagery relates to smell, gustatory imagery is about taste, tactile imagery deals with touch sensations, and auditory imagery concerns sounds. Examples are given for each type to illustrate how authors can use imagery to engage readers' senses and make descriptions more vivid. The purpose is to help students understand imagery and be able to identify and incorporate different sensory types into their own writing.