Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times
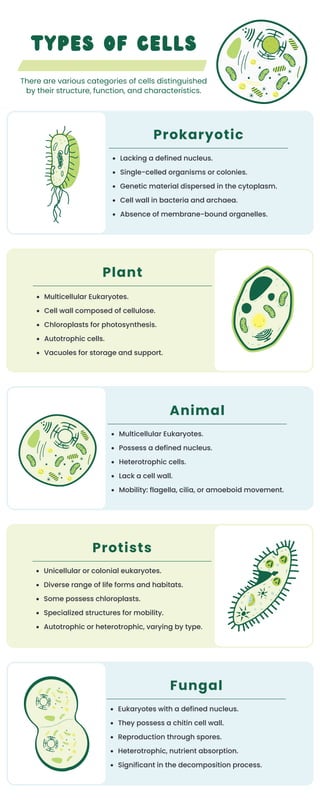
Cells can be categorized into prokaryotic and eukaryotic types based on structure and function. Prokaryotic cells lack a defined nucleus and organelles, while eukaryotic cells, which include plants, animals, fungi, and protists, have defined nuclei and can be autotrophic or heterotrophic. Different types of eukaryotic cells possess various structural features, such as cell walls and chloroplasts, contributing to their diverse functions and habitats.
