Embed presentation
Download to read offline



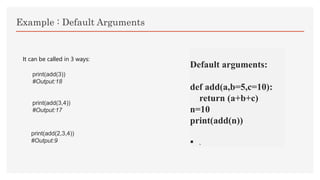
Default arguments allow functions to be called with fewer arguments by assigning default values if arguments are omitted. A function can have any number of default arguments, which should follow non-default arguments. Default arguments are defined using the assignment operator when defining the function and will be used if that argument is not passed to the function call, otherwise an overridden value in the call is used instead of the default.



