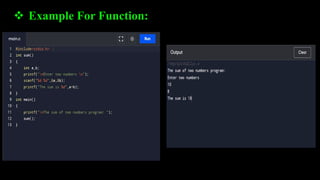
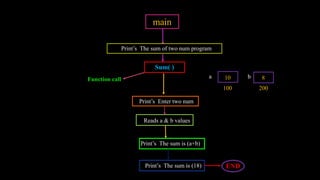
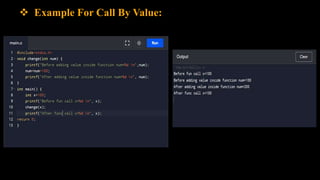
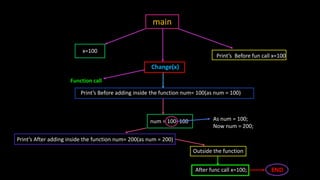
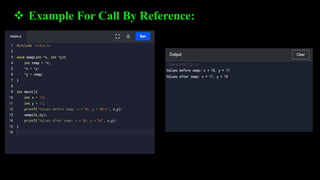
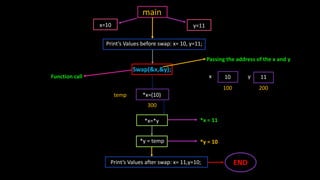
Functions allow programmers to organize code into reusable blocks to perform tasks. There are advantages like avoiding duplicated code, easy debugging. Functions can be predefined from libraries or user-defined. Parameters can be passed by value, where copies are used, or by reference, where the original variables are accessed. Examples demonstrate passing values vs references and how changes only affect the original variables for the latter.