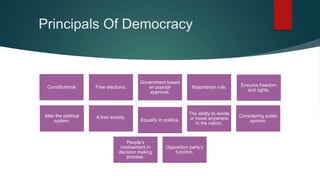
Democracy allows citizens to choose their government through free and fair elections held every five years. It is based on principles of social equality, individual respect, and popular approval of the government. Key characteristics include citizen control over the government, protection of basic human rights, and tolerance and compromise between competing views. While democracy ensures freedom and representation, it can also lead to instability, power struggles, and broken promises during elections.








![References:
carlinha183 (2012). Democracy characteristics. [online] Available at:
https://www.slideshare.net/carlinha183/democracy-characteristics [Accessed 20 Aug. 2022].
Iqra ali (2020). Principles of Human Rights. [online] Available at:
https://www.slideshare.net/IQRAALI58/principles-of-human-rights [Accessed 20 Aug. 2022].
Salman Nasär (2013). Democracy. [online] Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/salmansignin/democracy-
27814607
Mahesh Patil. (2017, July 5). Concept of democracy. https://www.slideshare.net/maheshjp05/concept-of-
democracy
NARESH KUMAR (2018). Features of Democracy with merits and demerits. [online] Available at:
https://www.slideshare.net/NARESHKUMAR1438/features-of-democracy-with-merits-and-demerits [Accessed
20 Aug. 2022].
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tst3bslides-220925090259-cc6251ca/85/TST-3B-SLIDES-pptx-10-320.jpg)