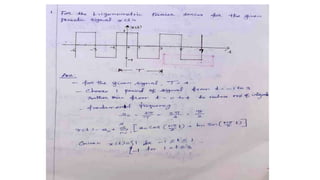
1. The document discusses Fourier analysis of continuous time periodic signals. It introduces Fourier series representation which expresses periodic signals as an infinite sum of sinusoids.
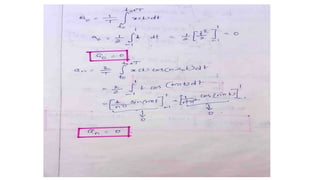
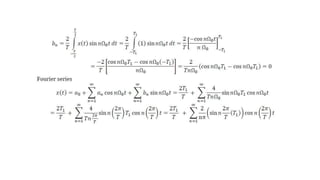
2. Continuous time periodic signals can be represented using a trigonometric Fourier series with coefficients that are calculated from the area under the signal over one period. Formulas for the cosine and trigonometric representations are provided.
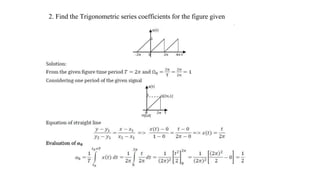
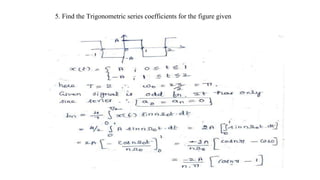
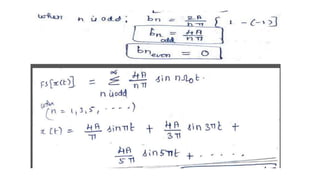
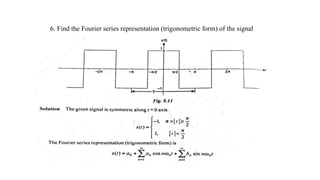
3. The document provides examples of calculating Fourier series coefficients for different periodic signals and deriving the Fourier series representation of a signal given its coefficients. Properties of continuous time Fourier series like symmetry conditions are also mentioned.