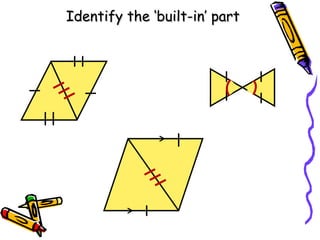
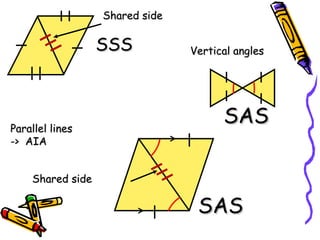
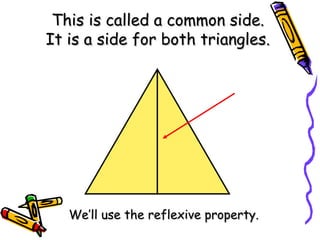
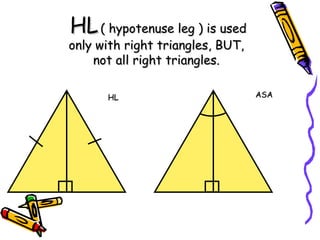
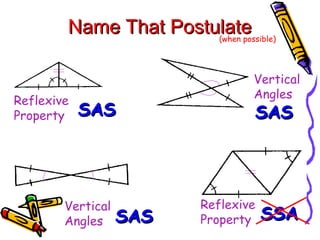
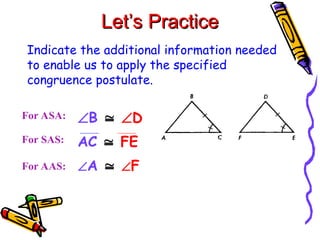
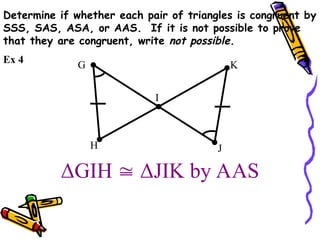
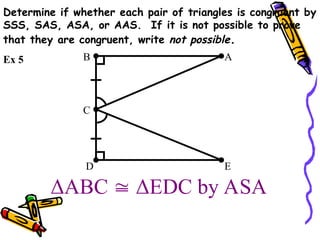
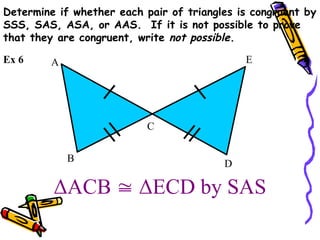
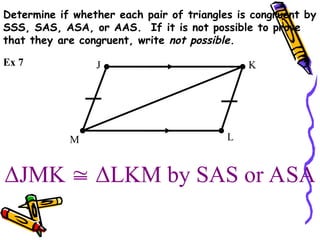
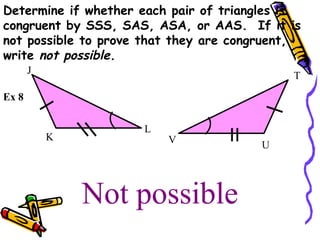
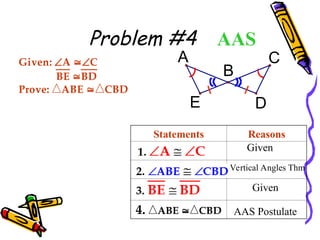
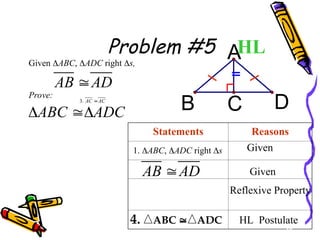
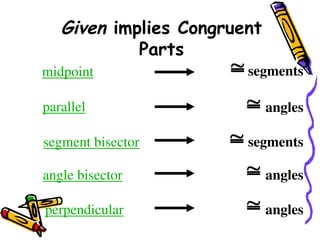
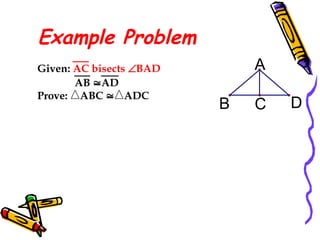
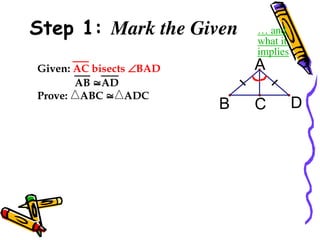
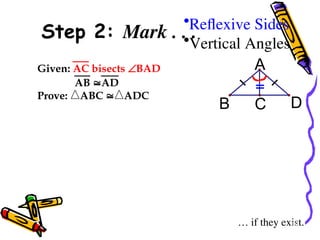
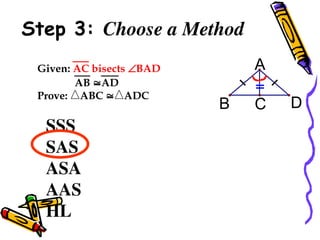
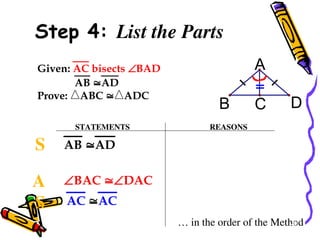
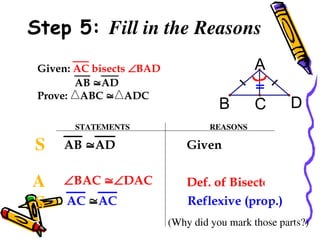
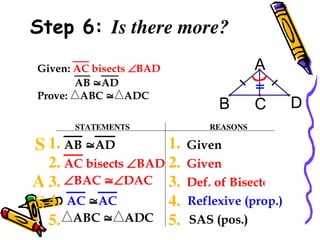
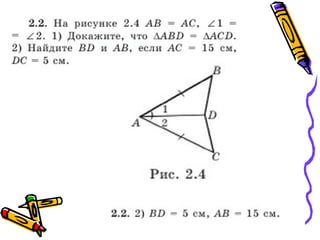
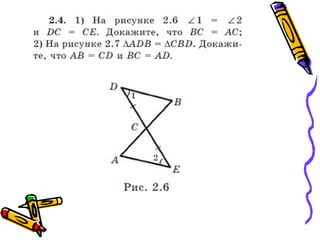
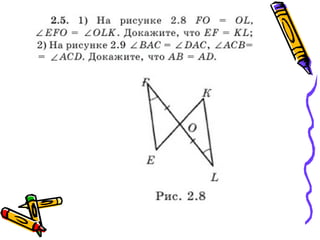
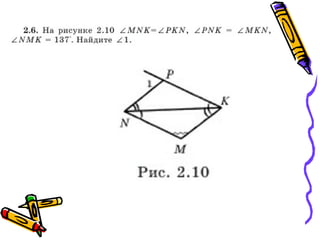
The document outlines methods for proving the congruence of triangles, including postulates like SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS, and HL specifically for right triangles. It describes the necessary additional information and common properties such as reflexive and vertical angles that aid in proving congruence. The document also provides examples and steps for constructing congruence proofs.