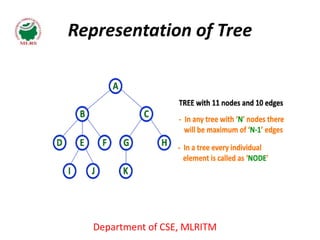
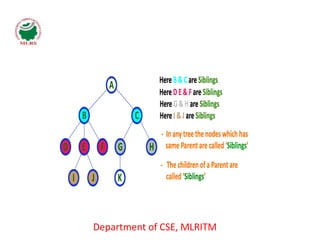
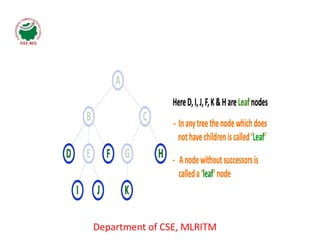
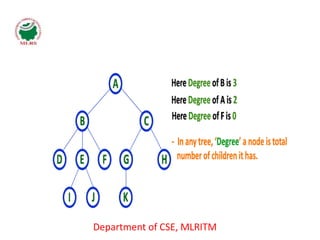
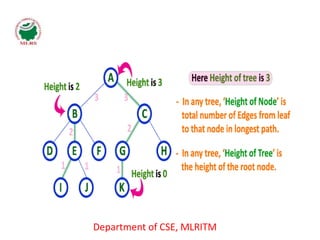
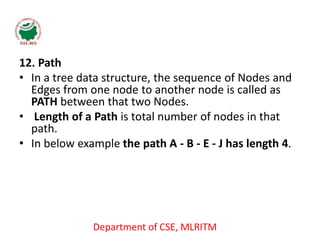
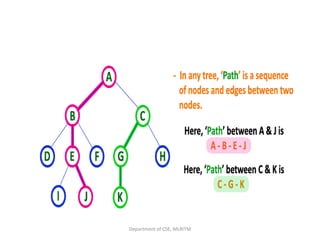
This document defines and explains the key terminology used in tree data structures. It describes that a tree is a non-linear hierarchical data structure composed of nodes connected by edges. The root node sits at the top of the tree and each node can have zero or more child nodes. Other terms defined include parent, child, leaf, internal and sibling nodes, paths between nodes, subtrees, and the levels, heights, depths and degrees of nodes.