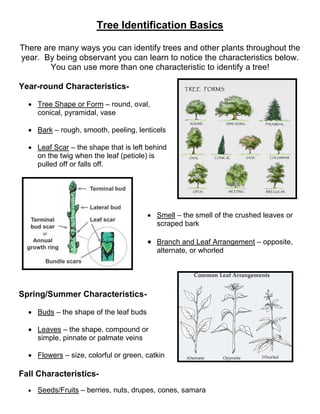
Tree identification can be done using characteristics that are present year-round, in spring/summer, or in fall. Year-round characteristics include tree shape, bark texture, leaf scars, smell, and branch/leaf arrangement. Spring/summer characteristics are buds, leaf shape/venation, and flowers. Fall characteristics are seeds, fruits, cones, and samaras. When identifying trees, it's important to look at multiple branches and characteristics and understand that appearances can vary based on age and environment.