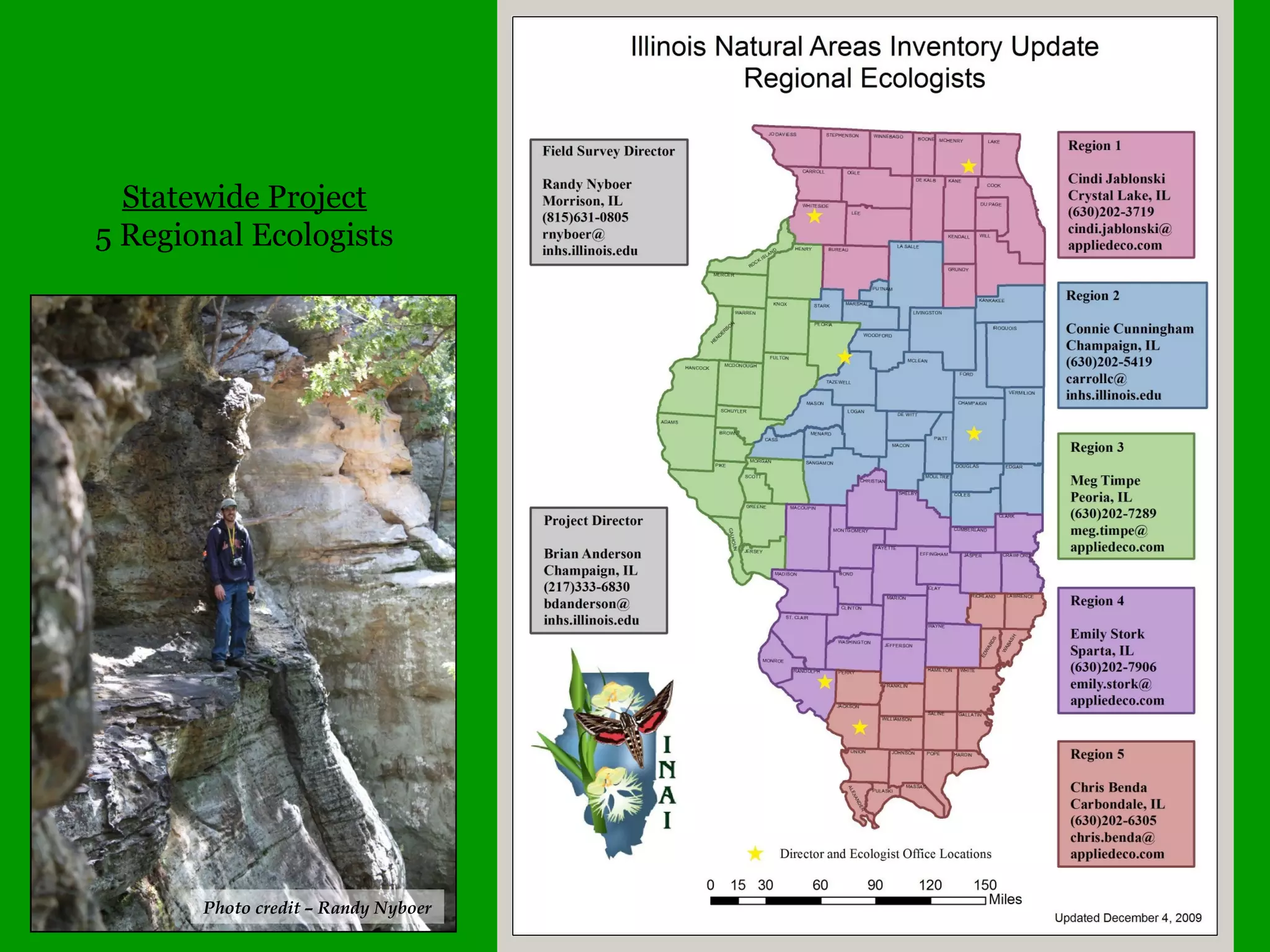
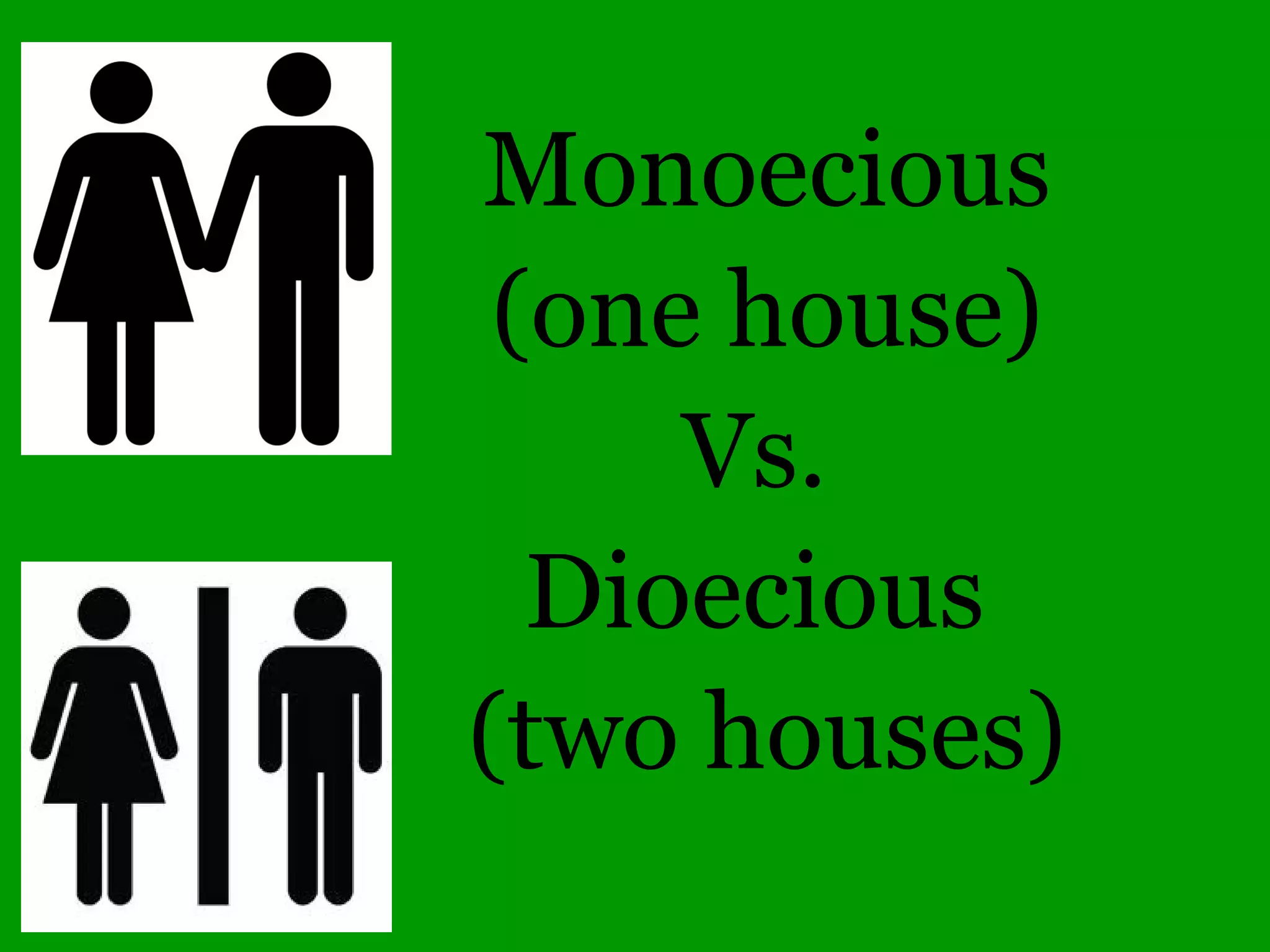
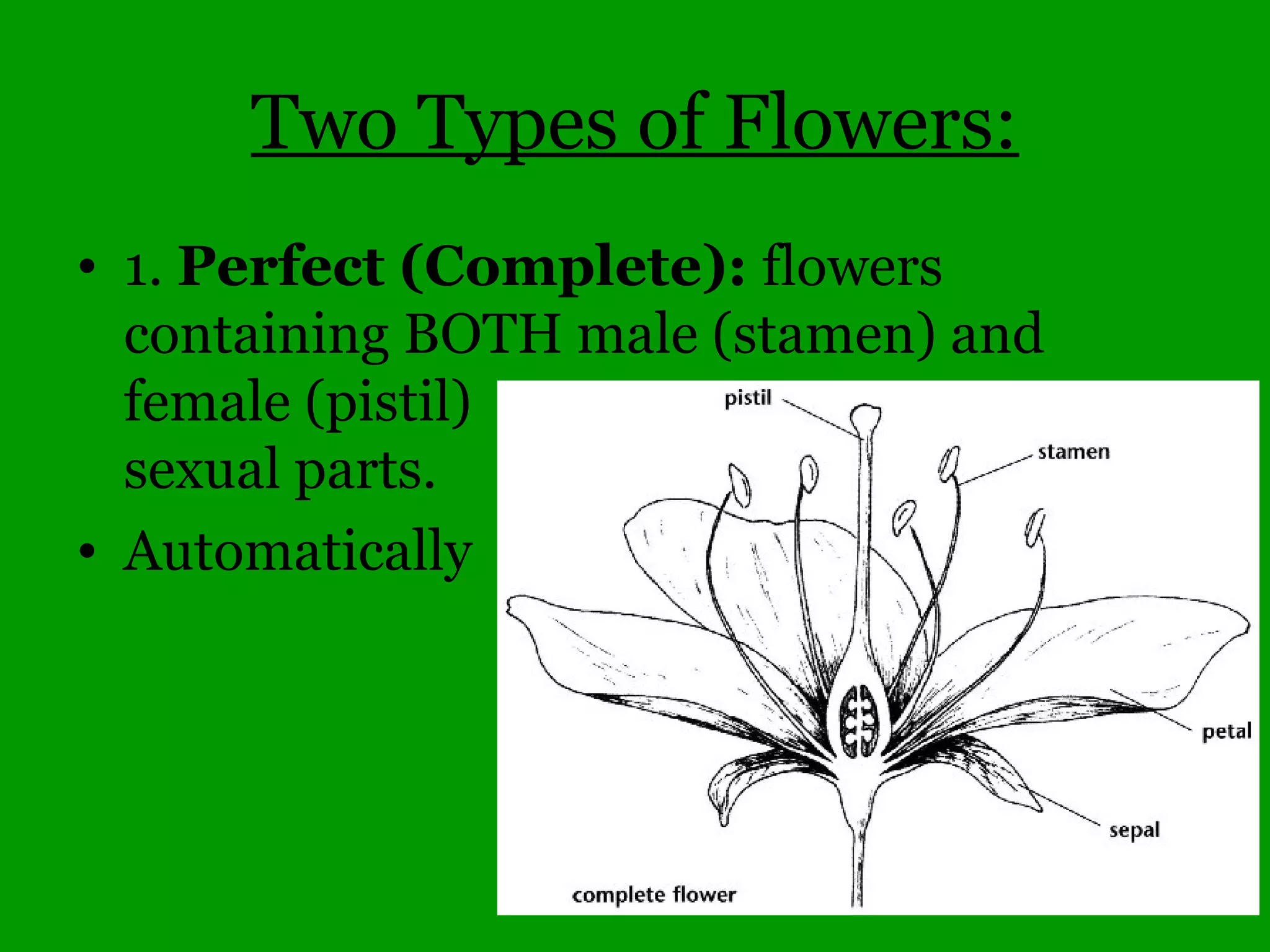
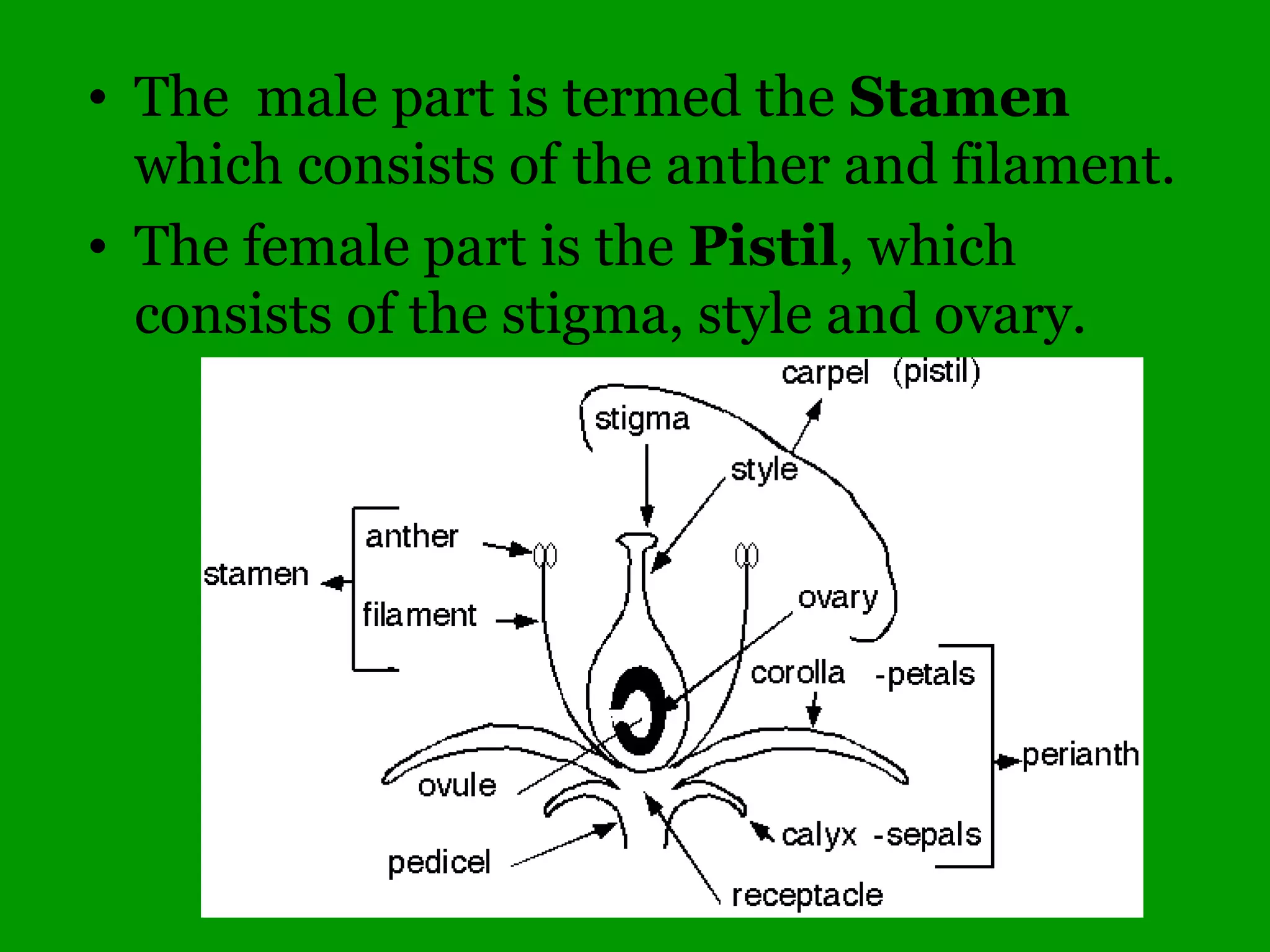
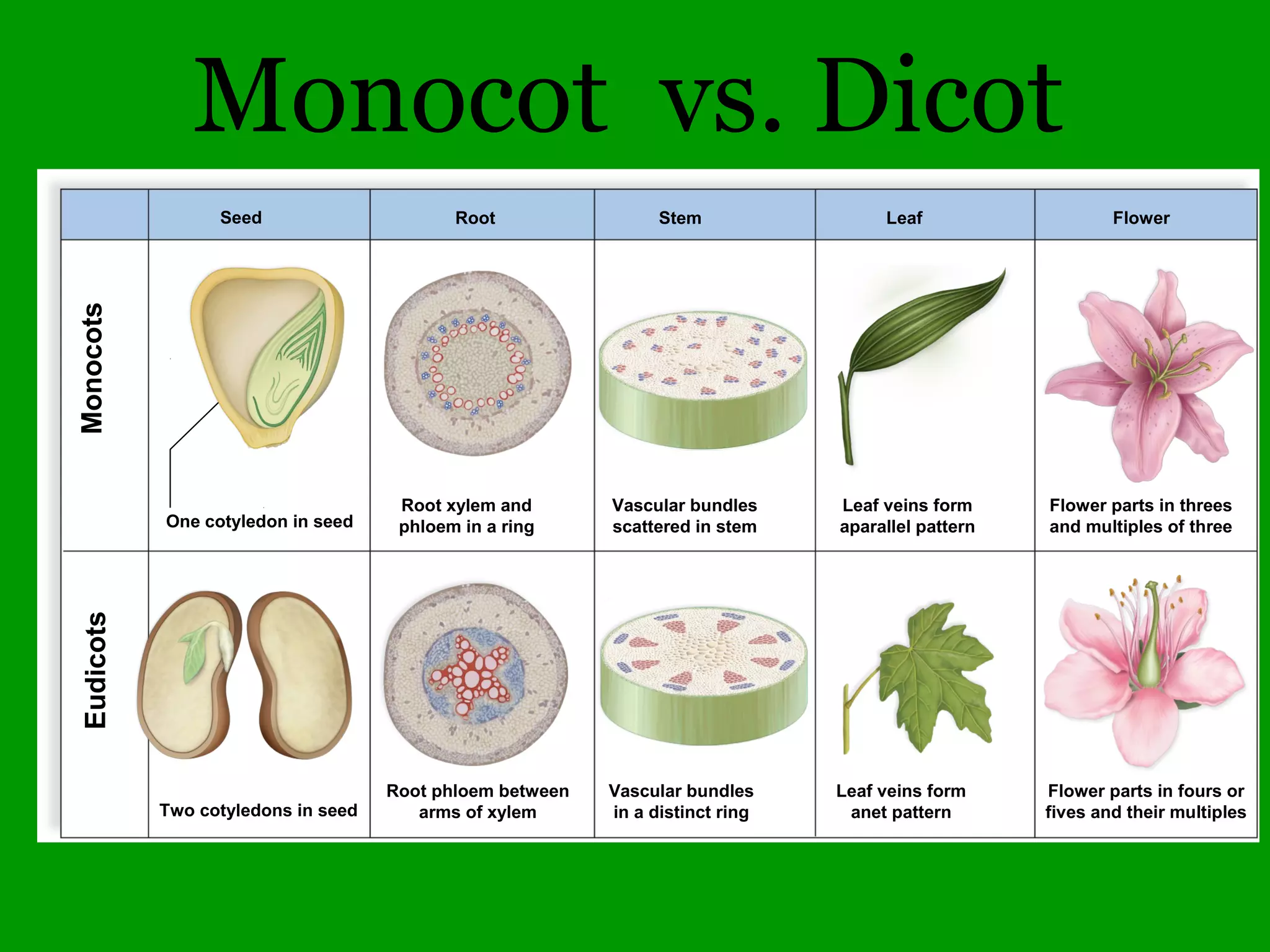
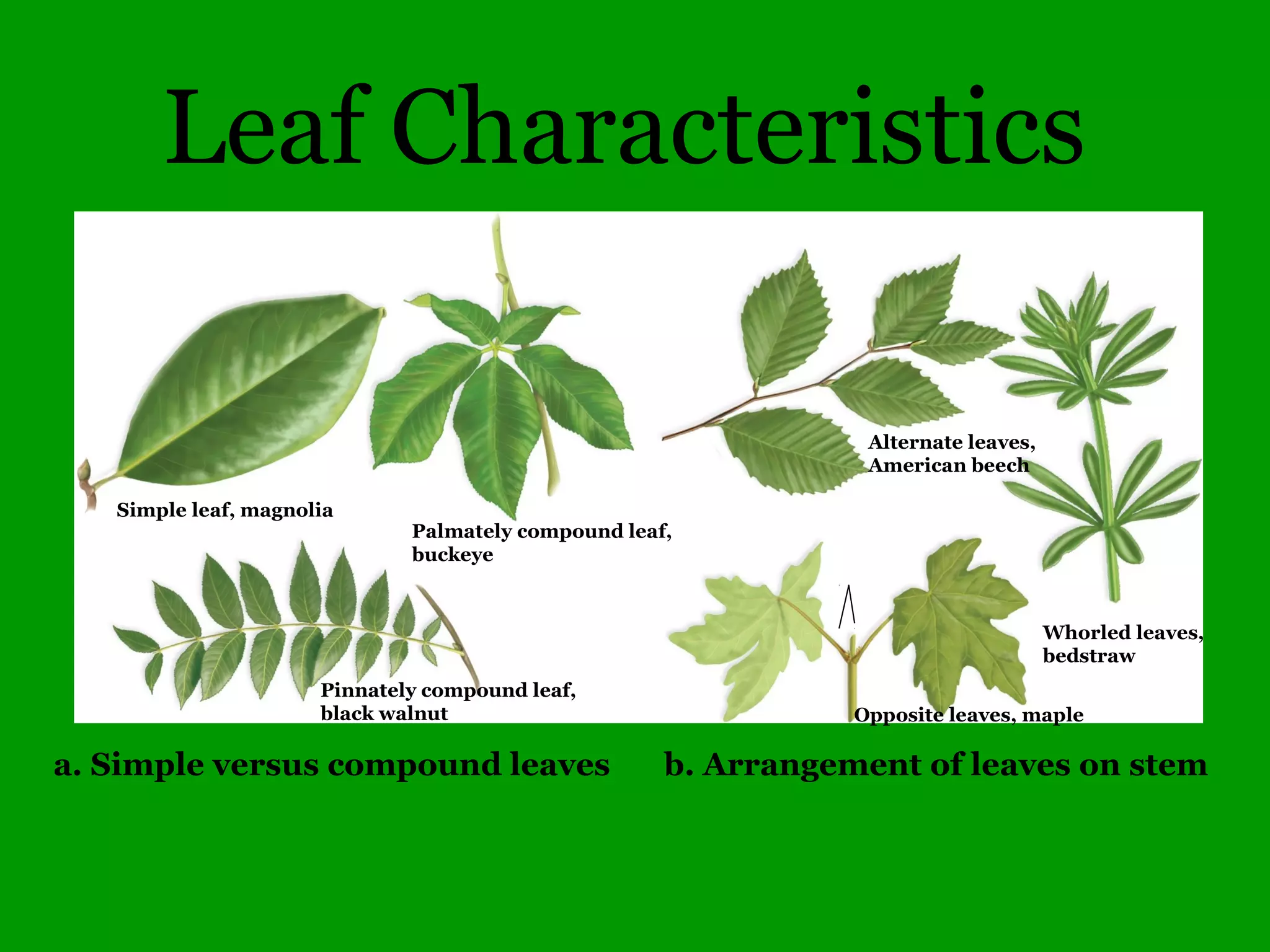
This document provides an overview of a tree identification and ecology course taught by Christopher Benda. It includes information about Benda's background and qualifications, as well as an outline of course topics like leaf and flower anatomy, plant taxonomy, dichotomous keys, gymnosperms and common woody angiosperms found in Illinois. The document lists many plant genera and species that will be covered, with a focus on identification and ecological information.