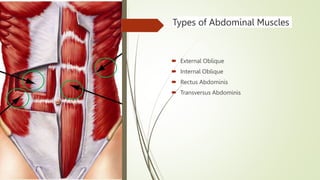
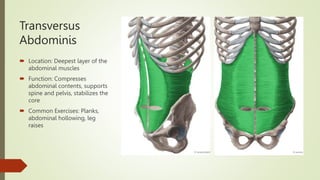
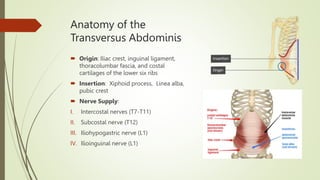
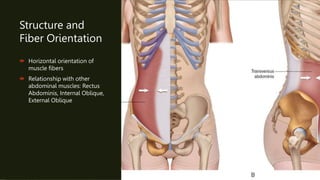
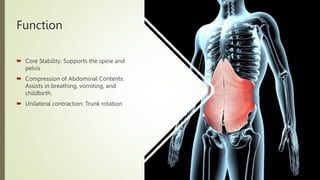
The document discusses the anatomy, function, and clinical importance of the transversus abdominis muscle, highlighting its role in core stability and abdominal compression. It details the muscle's origin and insertion points, nerve supply, and common exercises for strengthening. Additionally, it addresses the clinical significance of injury and rehabilitation strategies associated with the transversus abdominis.