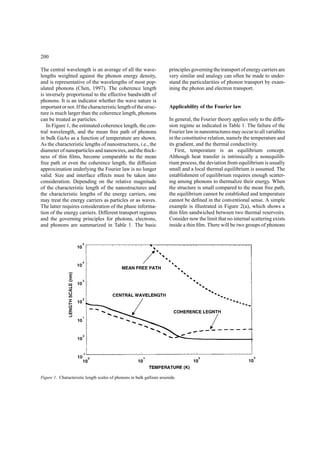
This document discusses heat conduction at the nanoscale and how it differs from macroscale heat transfer. At the nanoscale, the characteristic lengths of phonons (the main heat carriers in dielectrics and semiconductors) become comparable to nanostructure sizes. This invalidates the Fourier law of heat conduction, which assumes local thermal equilibrium. The document outlines different heat transfer regimes depending on relative sizes and discusses implications for thermal conductivity and applications like thermoelectrics where nanoscale effects could improve performance. Size effects are most dramatic in superlattices and thin films, while studies of heat transfer in nanowires and nanoparticles are still emerging. Understanding nanoscale heat transfer is important for optimizing nano-enabled technologies.