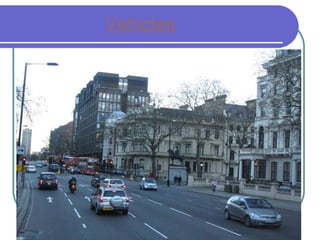
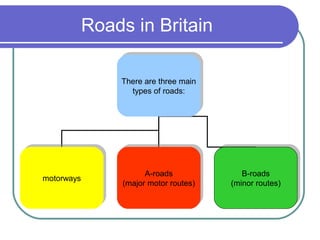
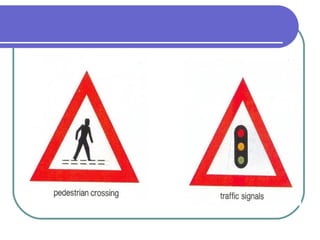
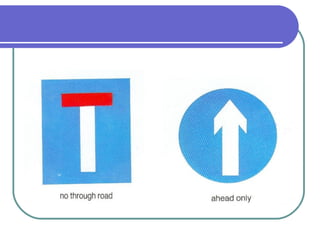
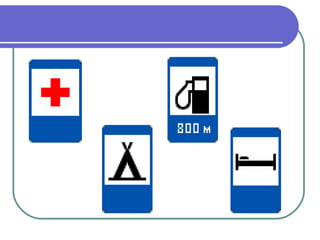
This document provides information about various modes of transport and roads in Britain. It discusses different types of vehicles including cars, buses, trains, boats, planes and more. It also describes different types of roads in Britain such as motorways, A-roads and B-roads. Additionally, it covers topics like traffic signs, the Highway Code and minimum driving ages in Britain. The document serves as a guide to transportation systems and road rules in the United Kingdom.
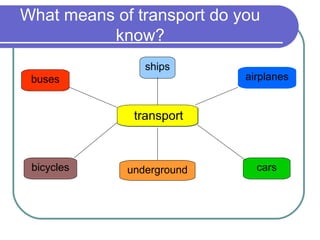
![Transport
[U] a system or
method for carrying
passengers or goods
from one place to
another](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transport-130218145911-phpapp01/85/Transport-2-320.jpg)
























![Traffic lights
also traffic signals n [usually
pl] coloured lights used for
controlling and directing
traffic, especially where one
road crosses another](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transport-130218145911-phpapp01/85/Transport-29-320.jpg)