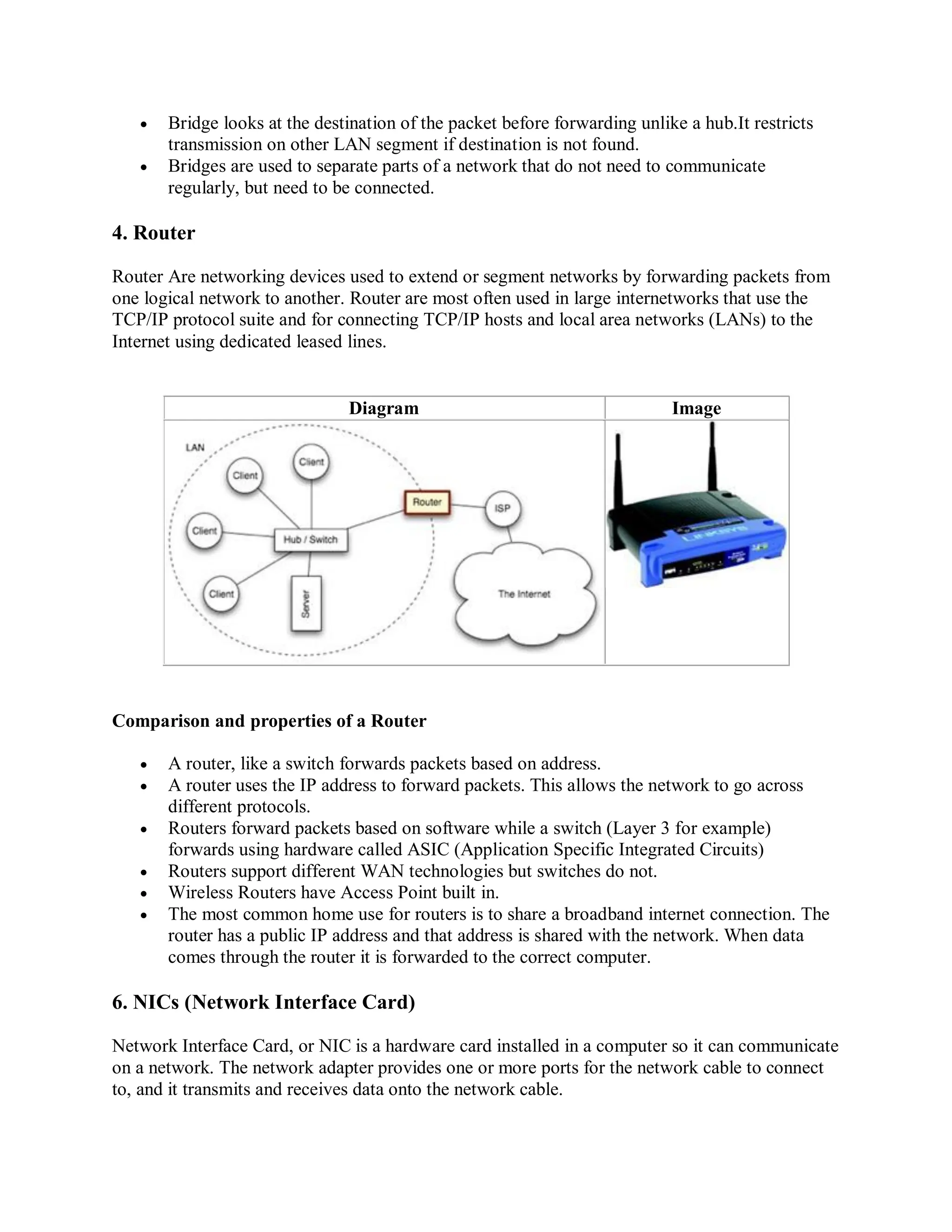
The document explains transmission media as pathways for data transfer within networks, categorizing them into bound (e.g., twisted pair, coaxial, fiber optic cables) and unbound (e.g., radio waves, microwaves, infrared). It further discusses LAN topologies—bus, ring, and star—detailing their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it covers networking devices such as hubs, switches, bridges, routers, and modems, as well as various types of websites including portals, news sites, and blogs.