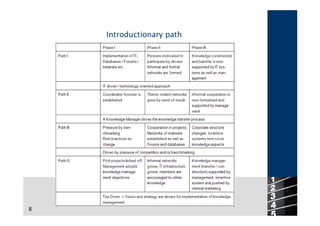
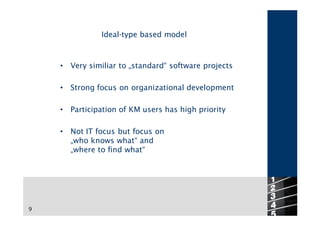
A manager can introduce knowledge management through a project management approach with phases for analysis, planning, and implementation. Another approach focuses on stakeholder involvement with technical and power promoters driving the process. A manager may also choose an introductionary path that is either technology-oriented, champion-driven, competitively pressured, or a top-down management decision. An ideal-type model emphasizes organizational development and user participation over IT focus. Main obstacles to knowledge management include high costs, lack of measurable success, information overload, and loss of user acceptance.