More Related Content
PPTX
Transformer_Visual_PPT_Placeholders.pptx PDF
Report on Transformers for class 12th 🥀.pdf PPTX
Transformer And Its Internal Structure and Transformer types.pptx PDF
kupdf.net_physics-project-on-quottransformersquot - Copy.pdf PPT
Tansformer @dheeraj upadhyay PPTX
PDF
Transformer_Introduction.pdf intro to them,turns ratio DOCX
Physics investigatory project Similar to Transformer_PresentationEngineering.pptx
PPTX
magnetism elctromagnetism .pptx PPTX
PPTX
Transformer_Presentation.pptx Electrical engineering department PPTX
Transformer_Presentation Electrical engineering department PPTX
Transformer_Presentation electrical engineering department DOCX
rushabh project physics 1.docx PPTX
PDF
DOC
PPTX
Transformer: Introduction, development, uses and calculations PPTX
PPT
TRANSFORMERS in physiotherapy high voltage and low voltage .ppt PPTX
Transformer ppt for micro-teaching (2).pptx PPTX
Transformer its types ,working,basic principle.pptx DOCX
Transformers Project report PDF
PDF
PPTX
Transformers basic electrical engineering PPTX
Transformer-History,Type And More Detail DOCX
Recently uploaded
PDF
ĐỀ MINH HỌA KỲ THI TỐT NGHIỆP TRUNG HỌC PHỔ THÔNG NĂM 2026 MÔN TIẾNG ANH 2026... PPTX
OXYGEN ADMINISTRATION/THERAPY ......pptx PDF
NCA New Family Orientation 2026 Dosemagen.pdf PPTX
Nanomaterials and its types - Dr.M.Jothimuniyandi PPTX
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS IN TEACHING SCIENCE.pptx PPTX
Statistical Data Analysis using R Programming.pptx PPTX
How to Create Opening Balance in Odoo 18 PDF
Geography unit 7-Population-Distribution`.pdf PPTX
Introduction of Carbohydrates - Dr.M.Jothimuniyandi PPTX
How to Create SMS Marketing Campaigns in Odoo 18 PPTX
How to Add or Remove Multiple Followers in a Records PPTX
Accounting Theory Group Presentation - Why Study Accounting Theory PPTX
Weaving Threads: Mapping Practitioner Theses to Understand Professional Becom... PPTX
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles - The Americas 1-18-2026 PPTX
NMR Spectroscopy: Principles and Applications PDF
BÀI GIẢNG POWERPOINT CHÍNH KHÓA PHIÊN BẢN AI TIẾNG ANH 6 CẢ NĂM, THEO TỪNG BÀ... PPTX
Activity on Job position in Odoo 19 Recruitment PPTX
Exploring car engine oil and lubricants purpose and functions DOCX
COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING OSCE CHECKLIST.docx PPTX
Ultrasound .pptx by Nagmani ojha (paramedical department)(Radiation technolog... Transformer_PresentationEngineering.pptx
- 1.
- 2.
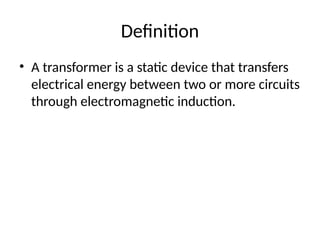
Definition
• A transformeris a static device that transfers
electrical energy between two or more circuits
through electromagnetic induction.
- 3.
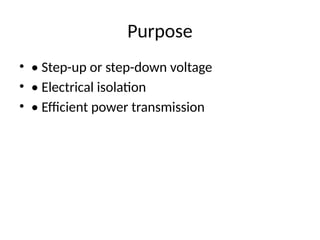
Purpose
• • Step-upor step-down voltage
• • Electrical isolation
• • Efficient power transmission
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
Types of Transformers
•• Step-up
• • Step-down
• • Power transformer
• • Distribution transformer
• • Auto transformer
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
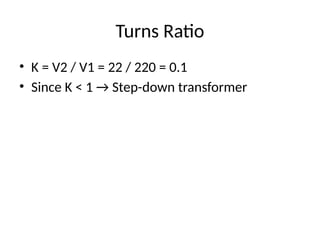
Turns Ratio
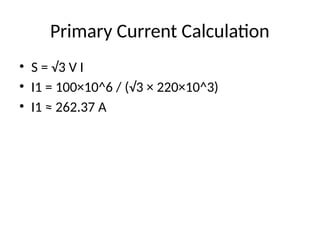
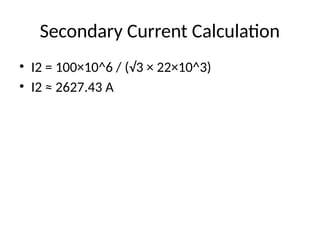
• K= V2 / V1 = 22 / 220 = 0.1
• Since K < 1 → Step-down transformer
- 15.
- 16.