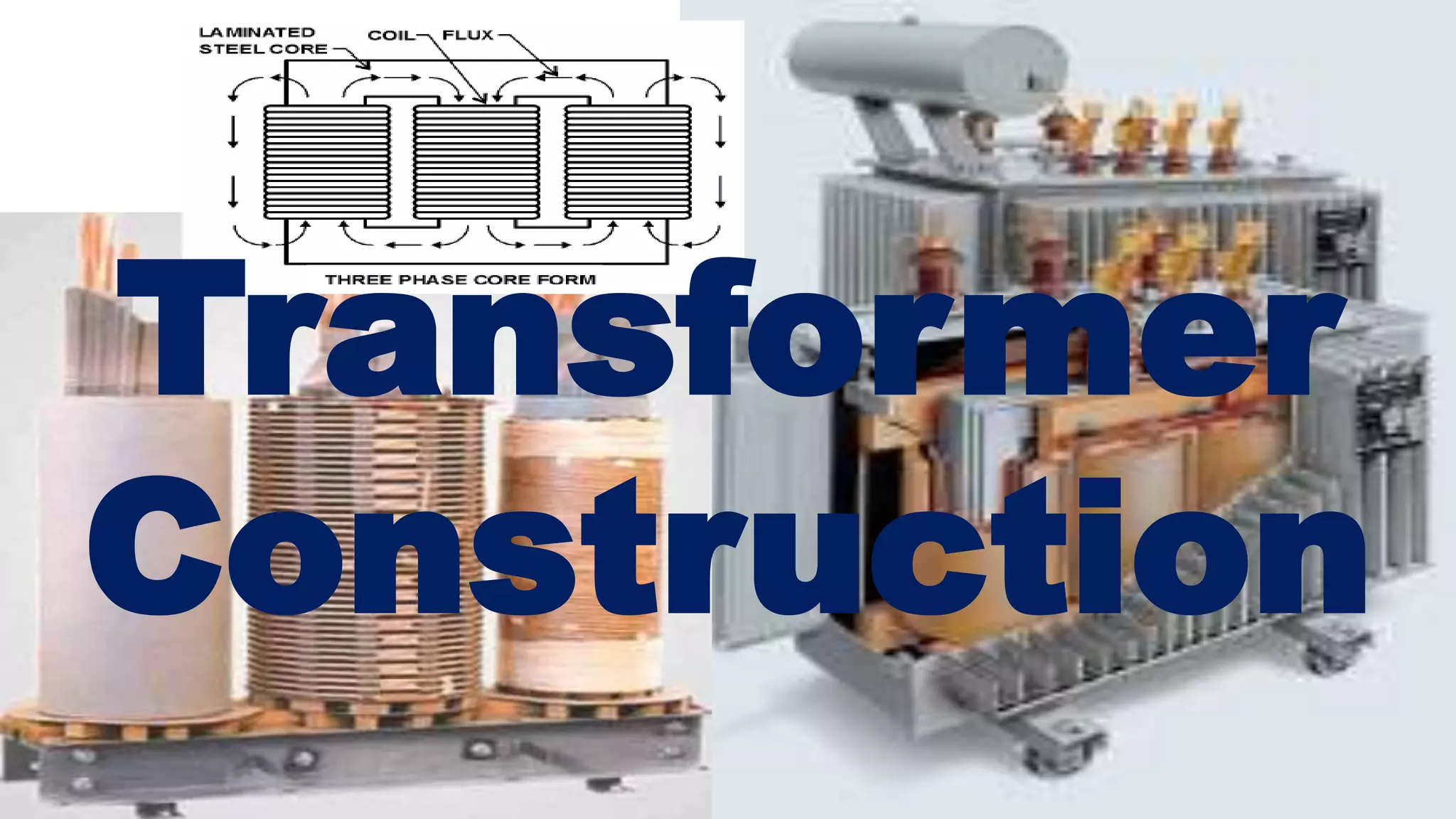
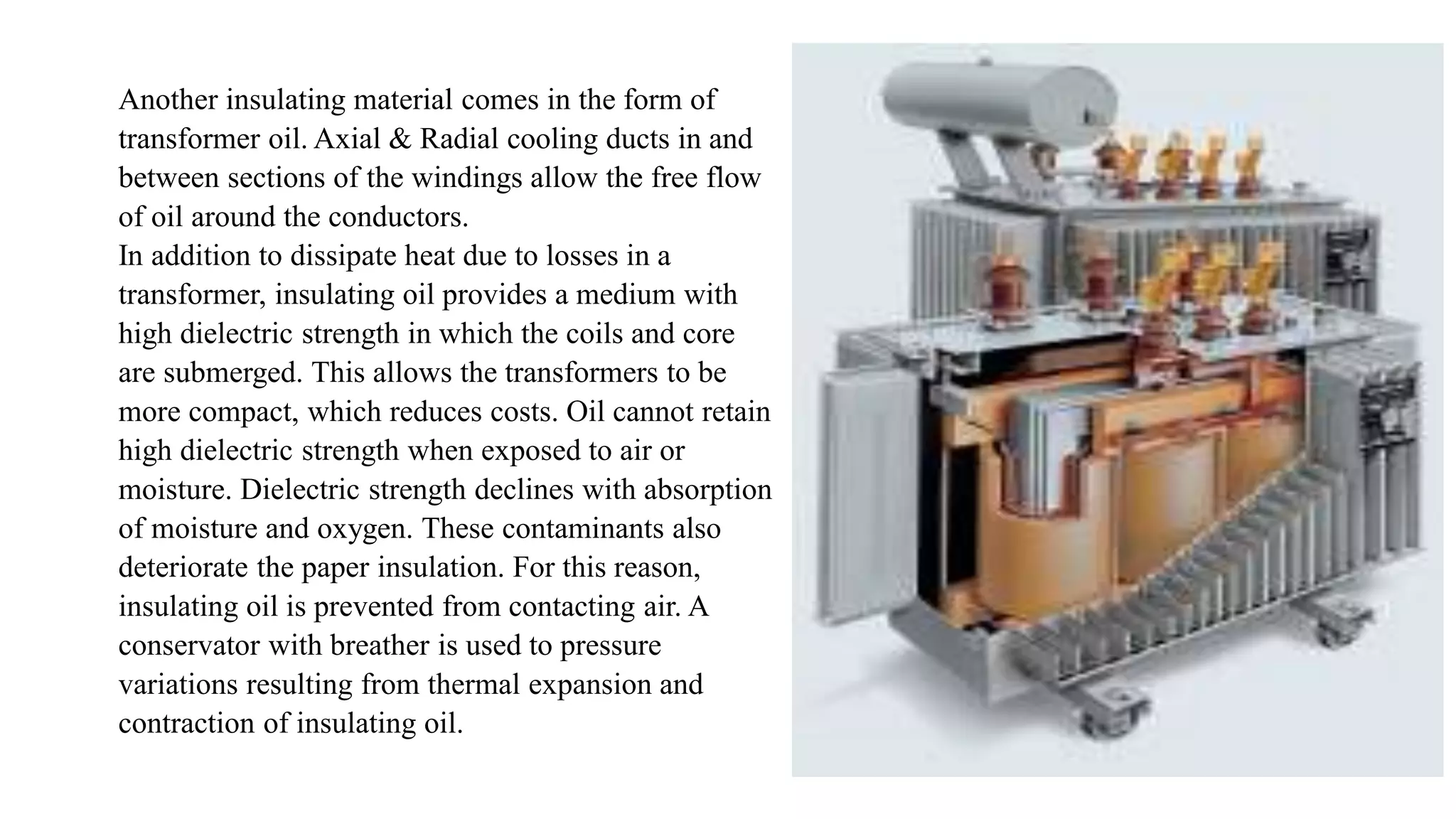
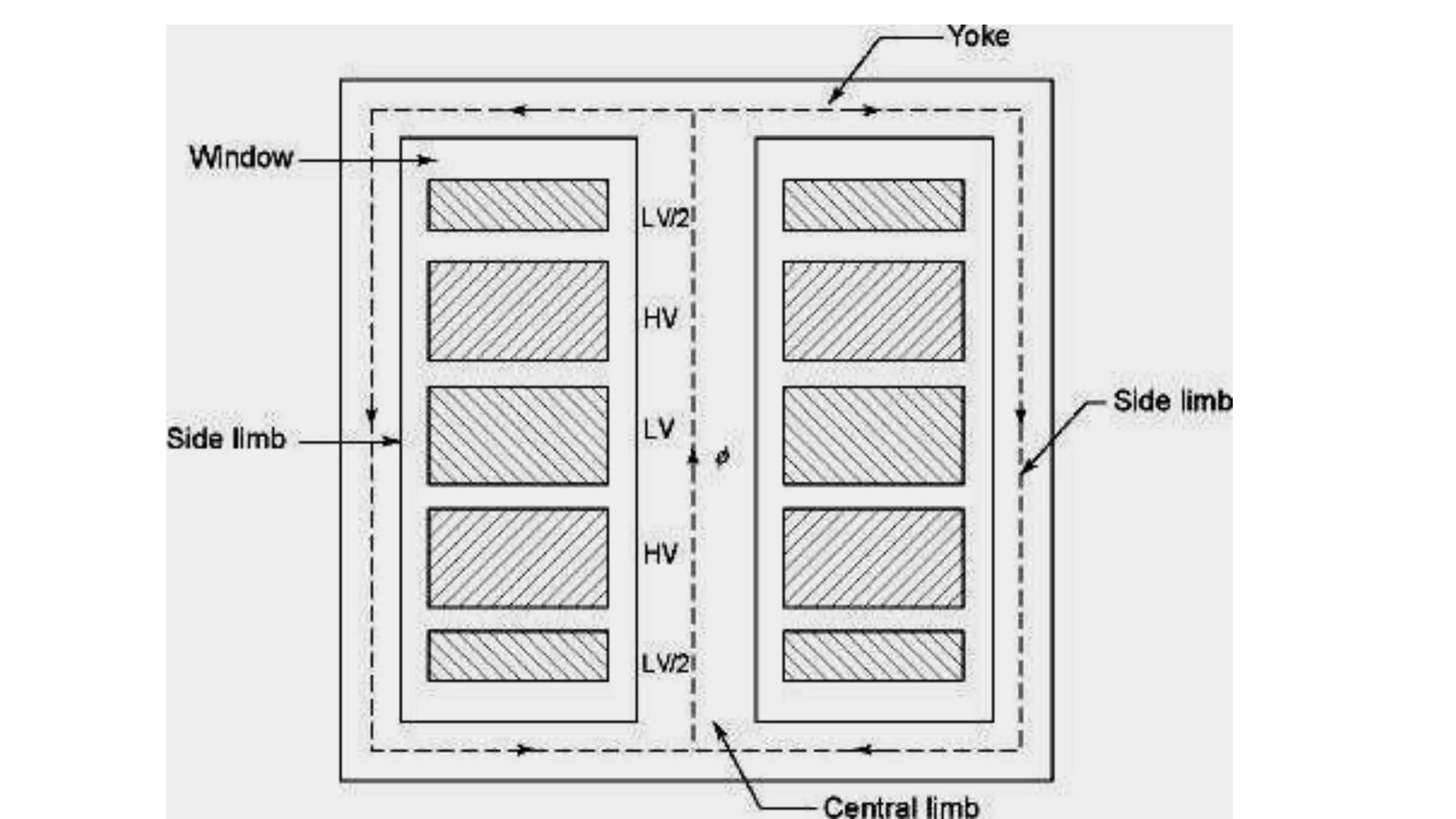
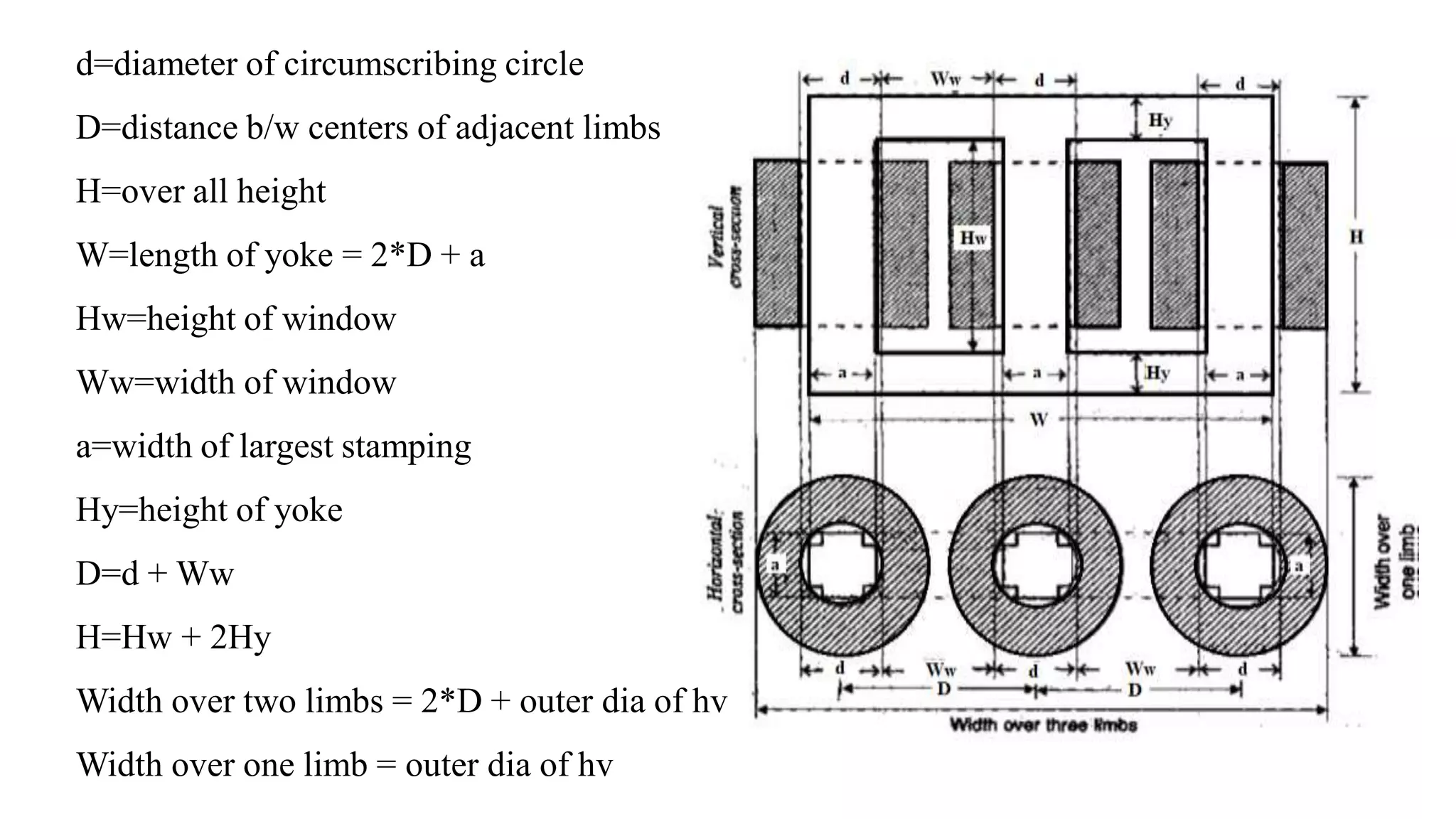
A transformer consists of a magnetic core and two electrical windings. Electricity from the primary winding induces electricity in the secondary winding through magnetic coupling. There are two main types of construction: core type and shell type. Core type transformers have concentric windings around the core limbs, while shell type have windings around a central limb with side limbs completing the magnetic path. Transformers change voltage and current levels, allow impedance matching, and provide electrical isolation between circuits. They are vital components for electric power transmission and distribution.