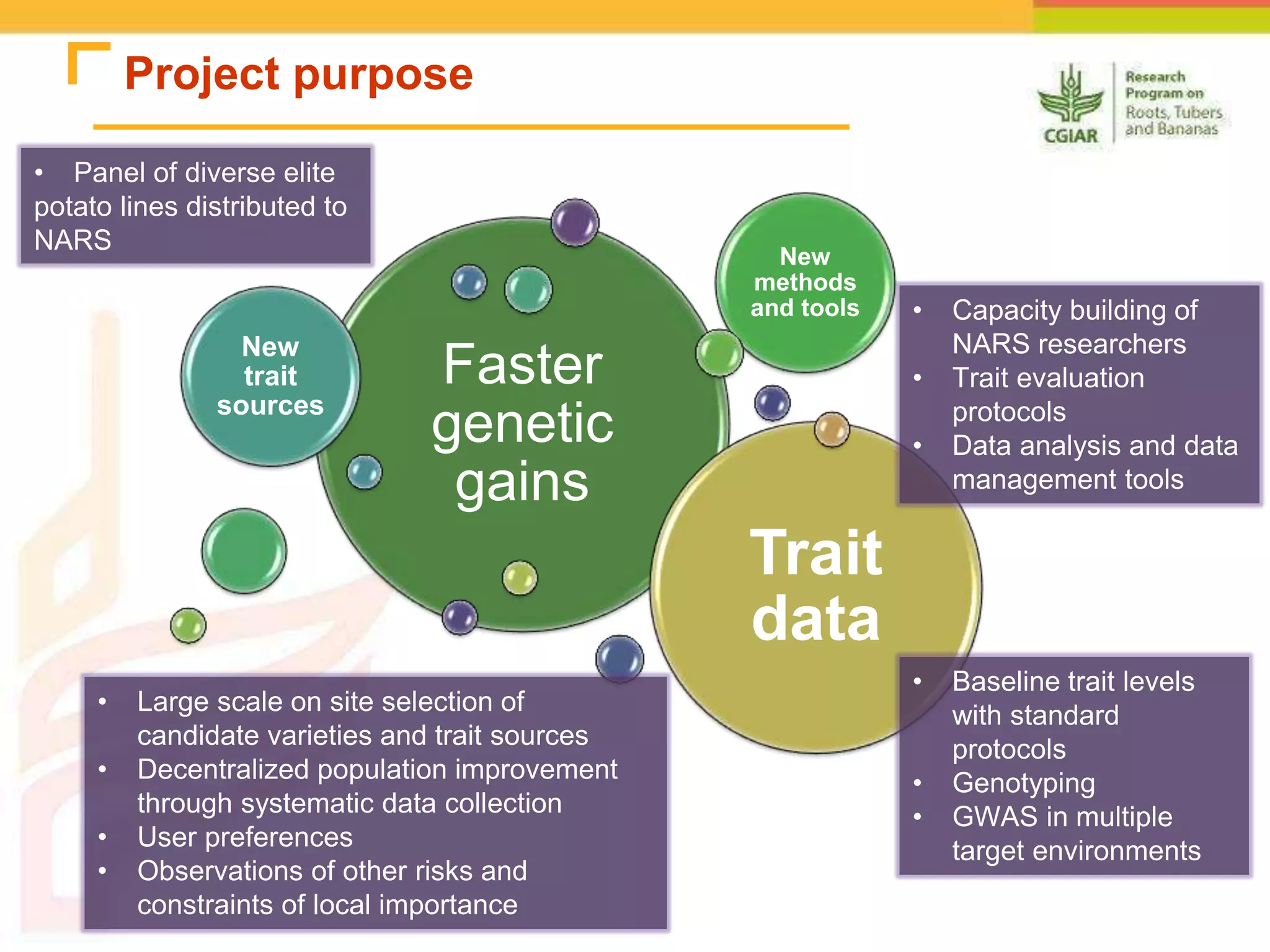
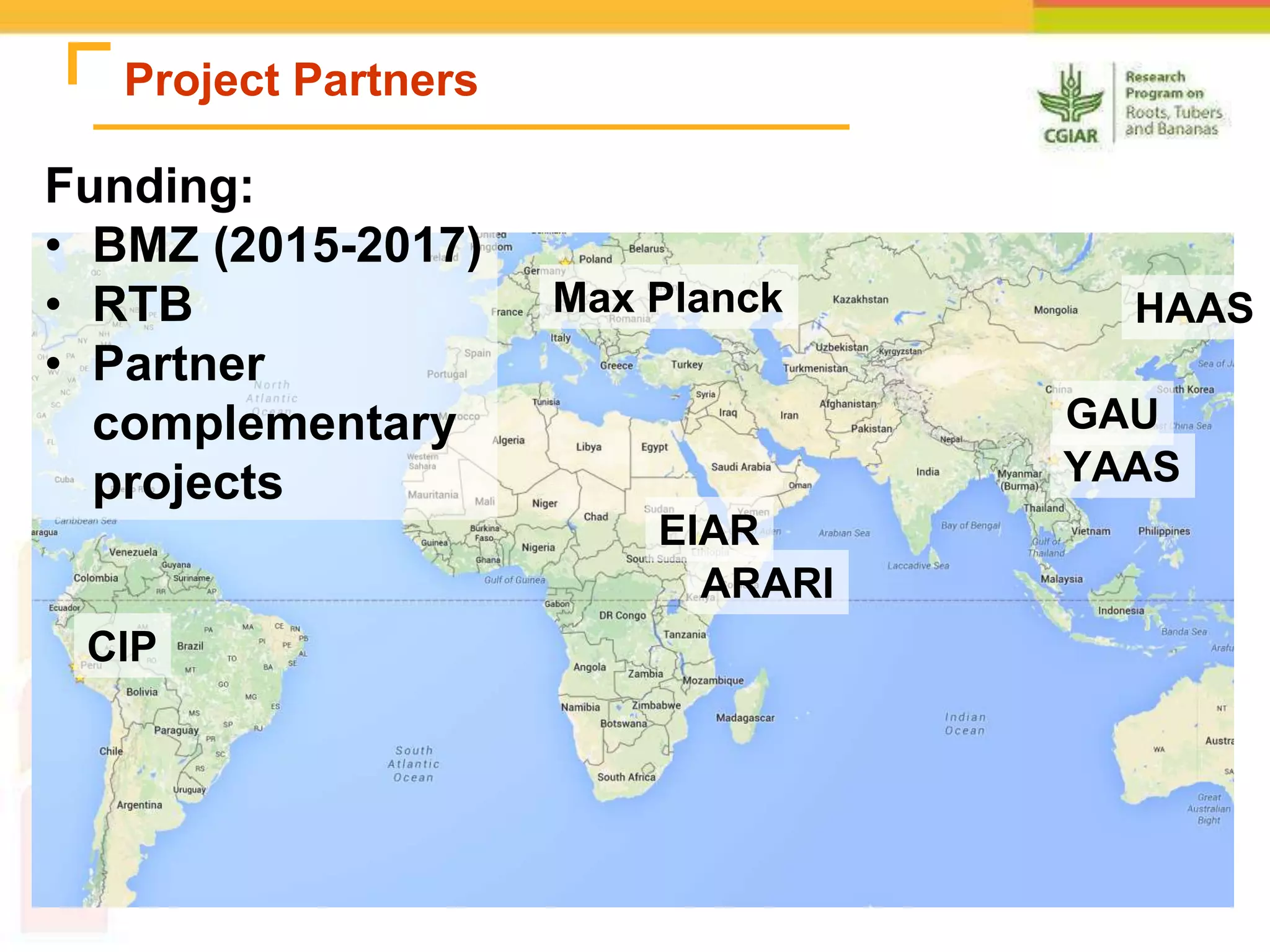
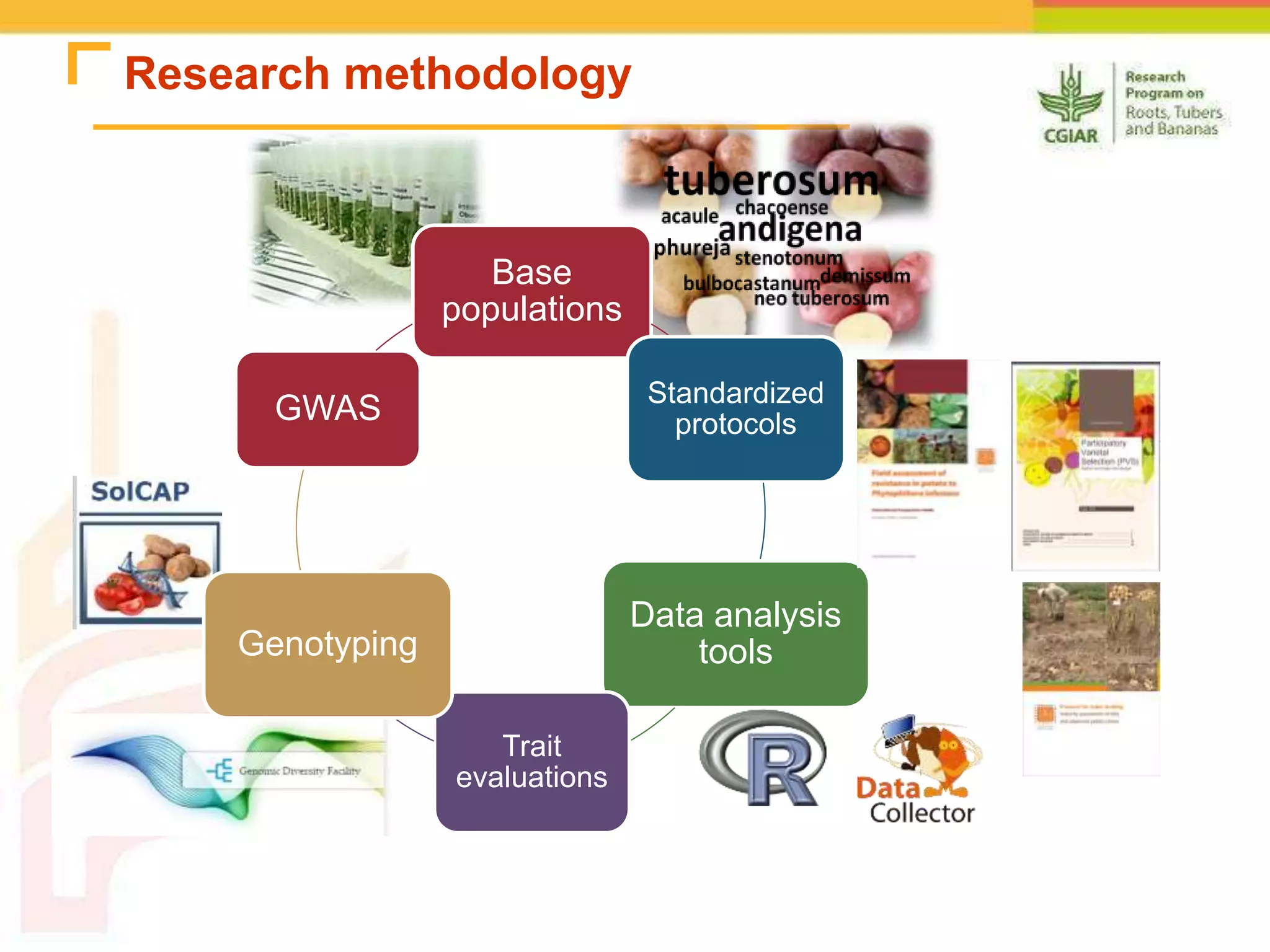
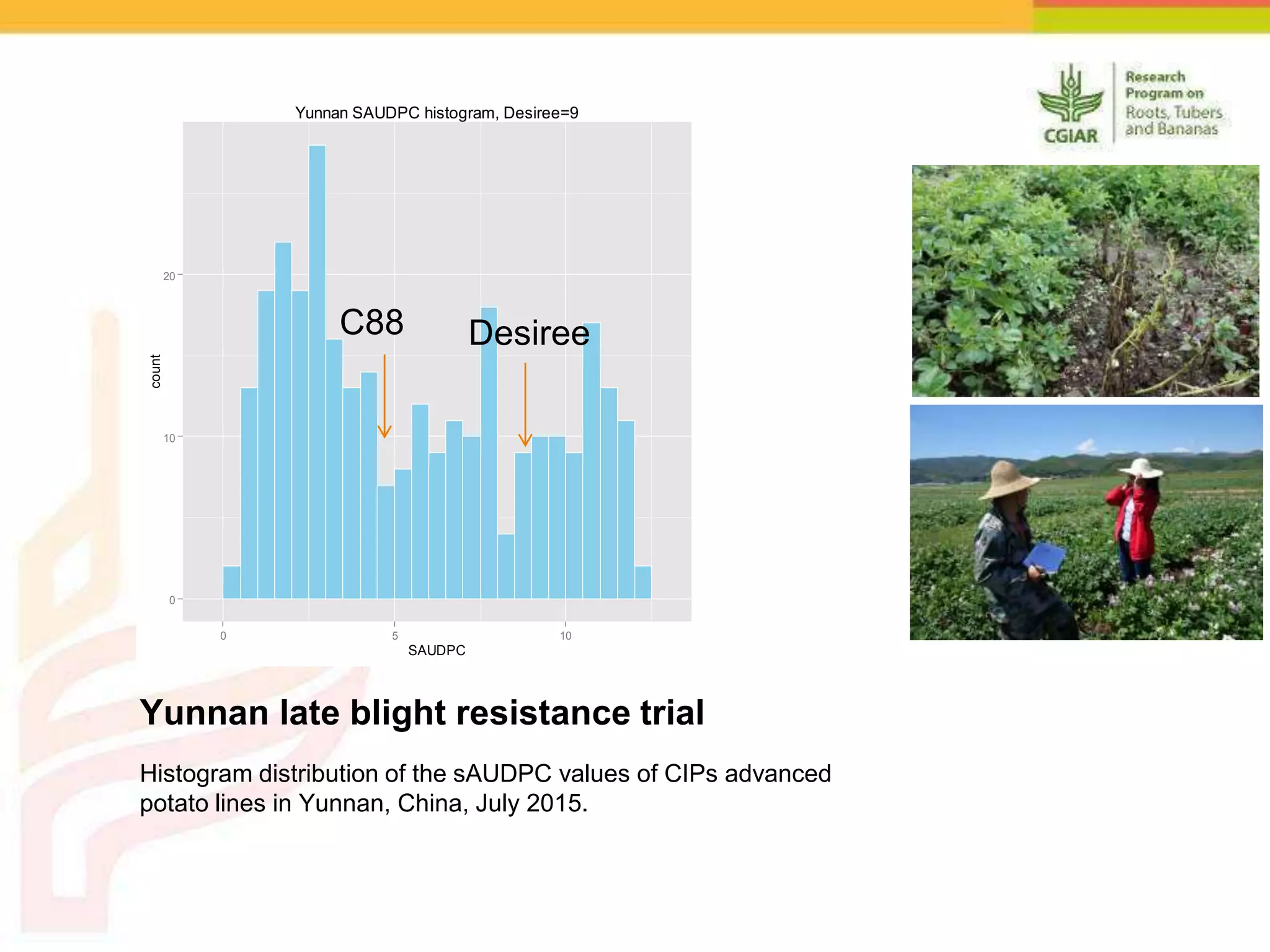
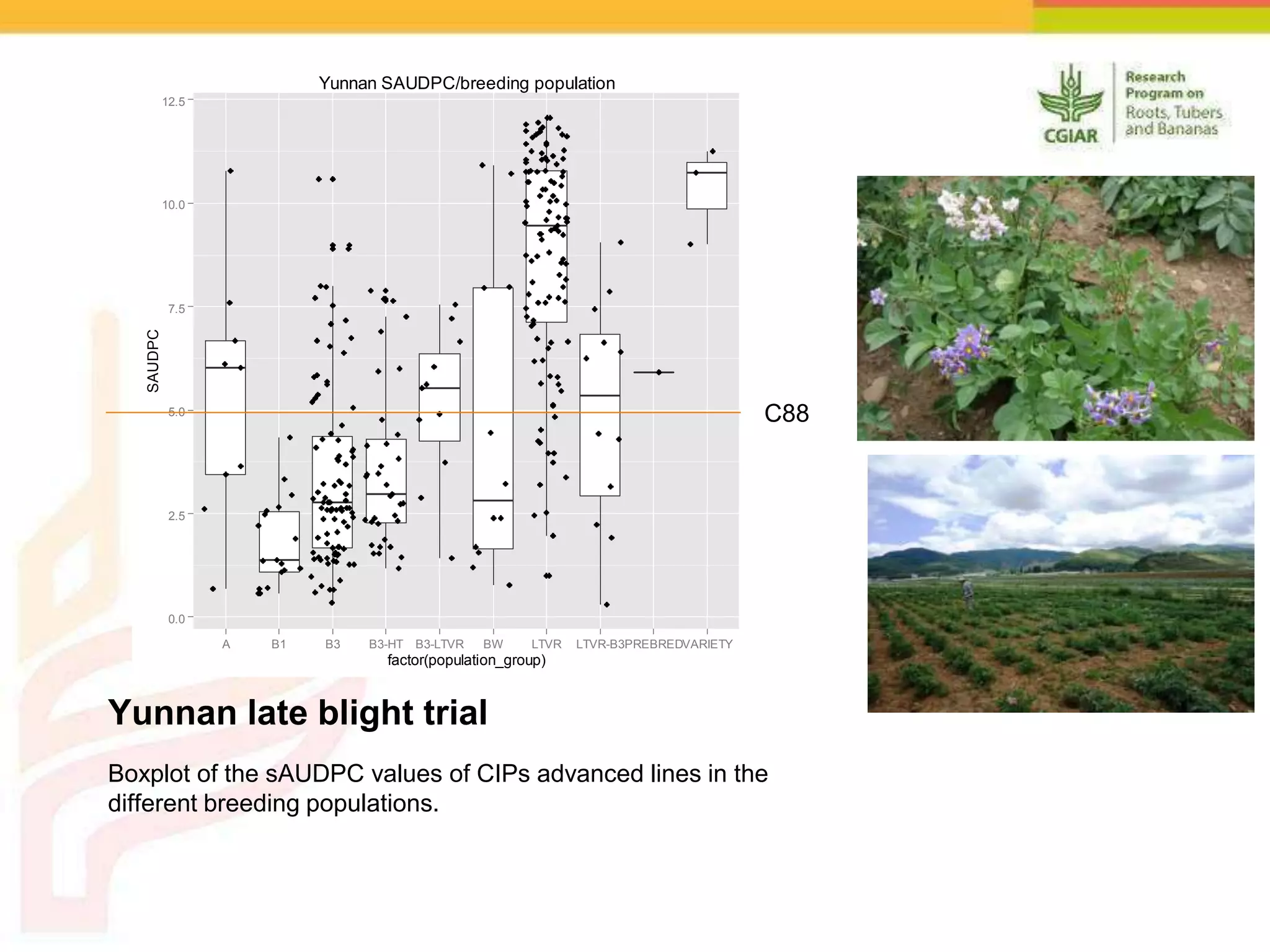
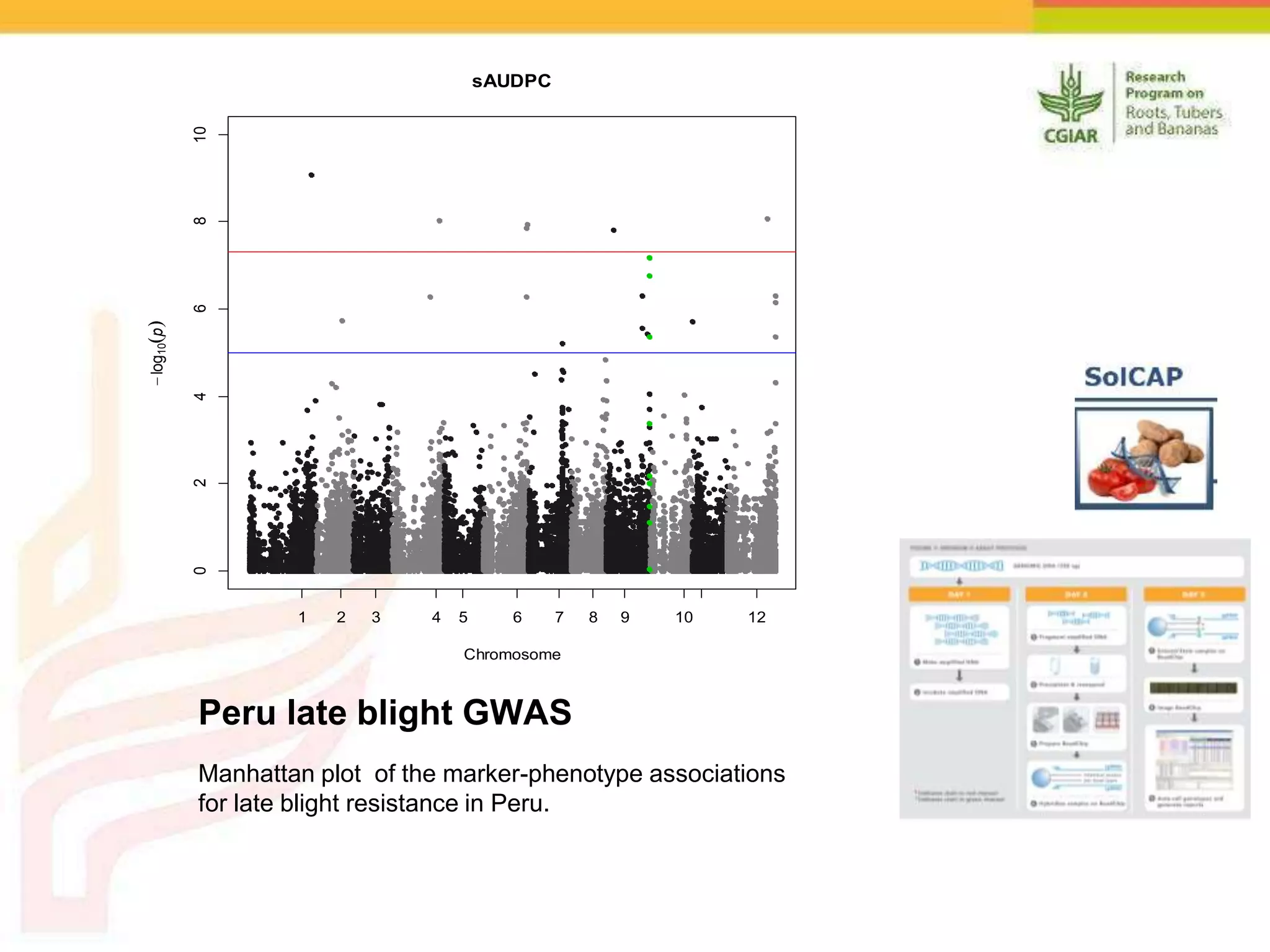
The document discusses a project aimed at enhancing potato yields in target regions through faster genetic gains, addressing the slow breeding process which can take 12-15 years. It outlines the methodologies for trait observation, evaluation, and data management, emphasizing collaboration among various research institutions and capacity building for local researchers. Key outcomes include the testing of genotypes based on user preferences and developing traits like late blight resistance and drought tolerance.